- Description and Features
- History of selection
- Main characteristics of the variety
- Purpose
- Ripening time
- Productivity
- Taste qualities
- Frost resistance
- Bunch
- Berries
- Disease resistance
- Methods of reproduction
- Cuttings
- By vaccination
- Layering
- How to plant correctly
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Site preparation
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering mode
- Top dressing
- Pruning and shaping the bush
- Mulching
- Garter
- Preparing for winter
- Protection from rodents
- Diseases and pests
- Mildew
- Oidium
- Gray rot
- Bacterial cancer
- Chlorosis
- Leaf roller
- Phylloxera
- Ticks
- Mole crickets
- May beetles
- Wasps
- Pros and cons of the variety
- Harvesting and storage
- Scope of application
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
Even novice gardeners can grow Victoria grapes. This variety is relatively easy to grow and produces abundant crops. It produces fruit even if the grower doesn't follow basic agricultural practices. To achieve the best possible results, it's important to understand its strengths and weaknesses, as well as the intricacies of planting and care.
Description and Features
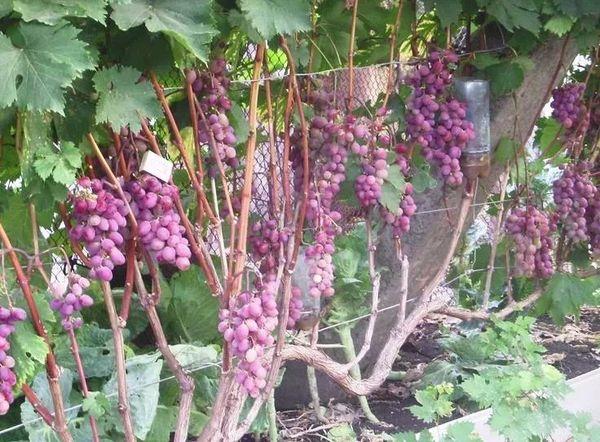
The Victoria grape is suitable for cultivation in temperate regions. This table grape variety has gained popularity thanks to its attractive and delicious berries. The harvest ripens in 115-120 days from bud break.
This early-ripening grapevine is distinguished by its robust underground growth, which allows it to withstand prolonged drought without harm. The plant is virtually immune to fungal diseases. The medium-sized Victoria grapevines have medium-sized, dark green foliage with characteristic pubescence.
Depending on the variety, the appearance of the Victoria group bushes has its own characteristics:
- Pink. The berries are purple and large. The grapes bear fruit reliably, year after year.
- White. This variety has been shown to have increased immunity to fungal infections. The fruits turn yellow with a greenish tint when ripe.
- Romanian grapes attract gardeners with their large clusters, weighing over 900 g. The berries come in white, yellow, and pink.
History of selection
Novocherkassk breeders at the Ya.V. Potapenko All-Russian Research Institute of Viticulture and Winemaking developed the Victoria grape. The parent varieties were frost-resistant and hardy varieties such as Save Vilar 12-304 and Vitis Vinifera. The result is a vine with a high degree of resistance to low temperatures, various diseases, and the ability to produce a large harvest early.
 Important! Victoria grapes can be successfully planted in the southern regions of Russia, Siberia, central Russia, and the Moscow region.
Important! Victoria grapes can be successfully planted in the southern regions of Russia, Siberia, central Russia, and the Moscow region.
Main characteristics of the variety
To obtain a stable and abundant harvest, it is necessary to study in more detail the main characteristics of Victoria grapes.
Purpose
The Victoria grape variety is a table grape with a pleasant flavor and distinct aroma.
Ripening time
Since the bushes begin to bear fruit early, harvesting is already possible in late August - early September.
The ripening process of the Victoria variety's fruits occurs almost simultaneously, but it is not recommended to rush their harvesting; it is better to let them remain on the vine for another 1-2 weeks to enhance their flavor.
Productivity
On average, a single bush can yield up to 50 kg of fruit. The productivity of the Victoria variety depends largely on agricultural practices; the better the care, the more fruit it produces.

Taste qualities
Sweet and aromatic berries ripen on the grape vines. As they reach consumer maturity, they develop muscat notes. The Victoria variety produces juicy, large berries.
Frost resistance
The bushes can withstand temperatures as low as -27°C. When grown in the Volgograd region, seedlings are best planted in areas protected by buildings or trees; additional insulation is not necessary. However, in temperate climates, Victoria grapes should be protected with agrofibre and spruce branches.
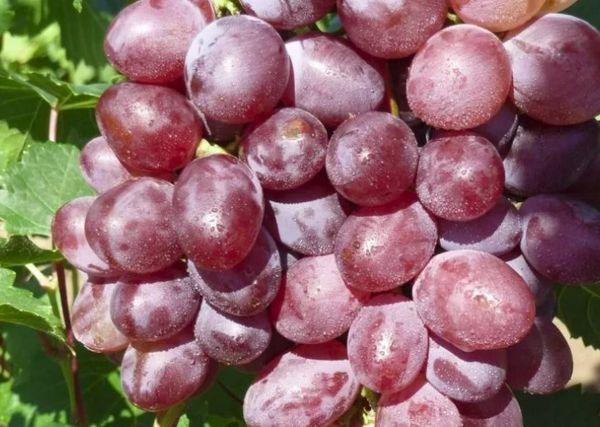
Bunch
The conical clusters are small and moderately loose. There are 2-3 clusters per shoot. Each cluster typically weighs no more than 700 g.
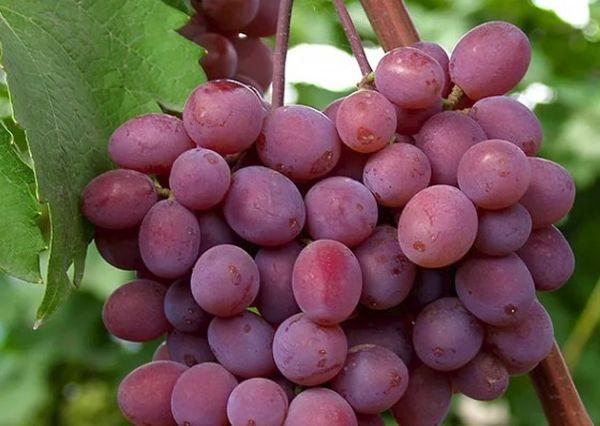

Berries
The fruits on the bush are a crimson-red color. They are oval, large, and 30 mm long. Each berry weighs 6-7 g. The skin is thin, and the flesh is fleshy and juicy, with a muscat flavor. The Victoria variety is prone to cracking.
Important! The sugar content of Victoria grapes ranges from 17-19%, and the acidity is 5-6 g/l.
Disease resistance
The bushes have sufficient immunity to most diseases. Grapes are resistant to gray mold, mildew (2.5-3 points), and powdery mildew (3 points). This variety is also resistant to grape budworm. To maintain healthy bushes, only two to three preventative measures are required per season.
Methods of reproduction
There are several methods for growing Victoria grapes; the main thing is to know the characteristics of each.
Cuttings
Victoria grape cuttings are taken in the fall from healthy vines. They should be 35-40 cm long and 0.5 cm thick. Each cutting should have 3-4 healthy buds. Store the cuttings in a damp cloth in a cellar or refrigerator until spring. In mid-March, the lower part of the cutting should be cut at a right angle, and the upper part at a 45°C angle, 3 cm from the bud.
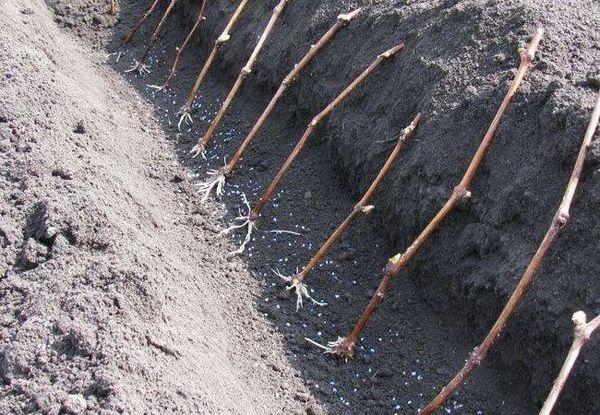

For better rooting, the grapes should be soaked in a container with a working solution of Kornevin and Heteroauxin for two days. Afterward, they are placed in a glass container with no more than 4 cm of water. After 21 days, roots will appear, and the cuttings should be placed in containers with fertile soil (a mixture of equal parts leaf mold, sand, and garden soil) and drainage. Victoria grapes are transplanted outdoors at the end of May.
By vaccination
This method involves using a scion with 2-3 buds, with the lower portion trimmed (wedge-shaped) to ensure a better connection with the rootstock. The upper portion should be treated with paraffin to retain moisture. A stump from an old bush is used as the rootstock.
The cut is cleaned to ensure a completely smooth surface, and a split is made in the center of the rootstock. The scion is inserted into this split, and the stump is tied together with rope or any other available material. To prevent infection, the joint should be treated with clay.
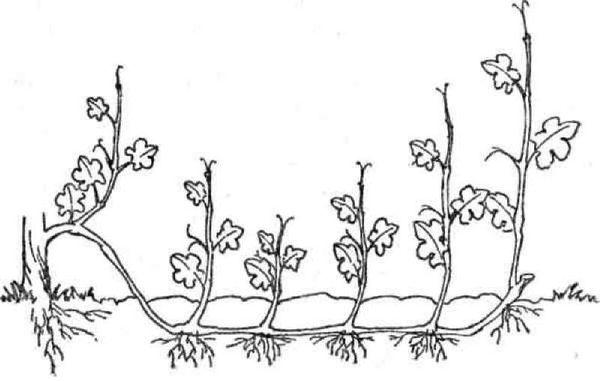
Layering
The bush's side shoots need to be dug in to allow them to develop their own root system. Once this occurs, they should be separated from the mother plant and planted in their permanent location.
The optimal time for carrying out this manipulation is spring and autumn.
How to plant correctly
The success of growing Victoria grapes largely depends on proper planting.
Recommendations for choosing deadlines
Planting begins in late March and ends in July (early March). If the young bush has developed leaves, planting occurs during the warmer months. For better and faster adaptation, Victoria seedlings are covered.
In the fall, planting should be done before the cold weather sets in. It's best to do this in mid-October. This depends on the weather conditions in your region.
Site preparation
Victoria grapes should be planted in a sunny clearing where there is no draft and where groundwater is close.
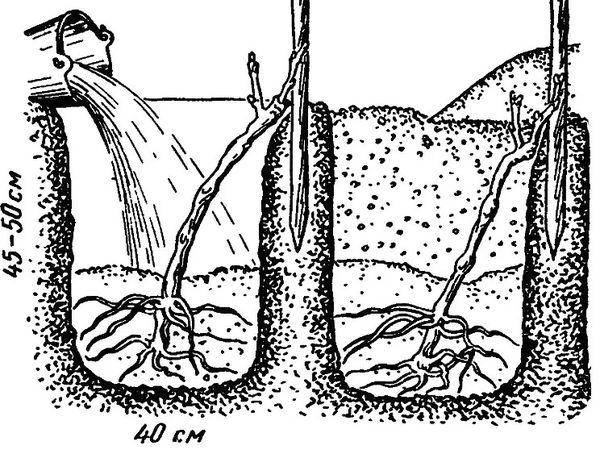
Preparing the site for planting seedlings in the spring should be done in the fall:
- clear the area of debris;
- dig a pit measuring 80×80 cm;
- Place a drainage layer (5 cm) on the bottom;
- pour fertile soil on top (10 cm layer);
- add compost (2 buckets);
- lay fertile soil (10 cm layer);
- using a mixer, mix all ingredients;
- cover with polyethylene.
How to select and prepare planting material
Before purchasing, inspect grapes for any damage or signs of disease. The vine should have at least three dark brown roots.
A couple of hours before planting, it's recommended to soak the seedling in a solution of Kornevin or another rooting stimulant. Then, immerse it in a clay slurry to prevent the roots from drying out.
Planting diagram
The landing algorithm involves the following steps:
- Open the hole.
- Remove a layer of soil.
- Place a young bush in the center.
- Straighten the root system.
- Install a support (peg) near the seedling.
- Sprinkle with soil and compact it.
- Water and mulch with sawdust and peat.
Important! Do not bury the root collar of the bush when planting; it must be above ground level.

Care instructions
Obtaining large fruits from Victoria grapes is only possible with proper care.
Watering mode
Although the Victoria grape variety can tolerate drought, it requires watering three times during the summer. Two to three buckets of water are used per plant. The final soil watering should be done in early October.

Top dressing
Fertilize in the fall using potassium salt (20 g per square meter) and superphosphate (40 g per square meter). In the spring, apply ammonium nitrate (15 g). During the active growth period, add bird droppings diluted in 10 liters of water. Wood ash is applied at the end of the season at a rate of 100 g per bush.
Pruning and shaping the bush
In the fall, dead shoots and dried fruit should be removed. Branches longer than 20 cm are removed first, while longer ones are shortened by a tenth. To form a fruiting stalk, tall shoots should be shortened to 12 buds, and lower shoots should be left with no more than 5.
Mulching
To retain moisture and control weeds, mulch bushes with wood shavings, compost, or peat. Avoid adding coniferous waste to the tree trunk area, as it promotes soil oxidation. The layer should be 5-9 cm thick.
Garter
This procedure is performed in the spring, after the bush is uncovered. The green staking is done when the shoots reach 35-40 cm in length. Subsequent staking is continued as the vine reaches the top tier of wire.

Preparing for winter
Before the cold weather sets in, dig a trench in the area, lay the vines, and cover them with sheets of roofing felt, slate, or even polyethylene. In the spring, when the weather warms up, remove the covering to prevent the plant from overheating. If there's a risk of frost, protect the uncovered bushes with hay or dry branches, and fumigate them with smoke.
Protection from rodents
Alternatively, grapes laid in trenches can be protected from rodents using pine branches. Place them on all sides. Traps in the form of plastic bottles coated with vegetable oil can be placed nearby.
Diseases and pests
At the first sign of disease, you need to immediately begin treating the bushes.
Mildew
The disease can be detected by the presence of oily, yellowish spots, which eventually develop into a whitish fluff. Bushes are treated with copper sulfate (5%). For prevention, use Bordeaux mixture and Ridomil when the vines reach 20 cm and after flowering.
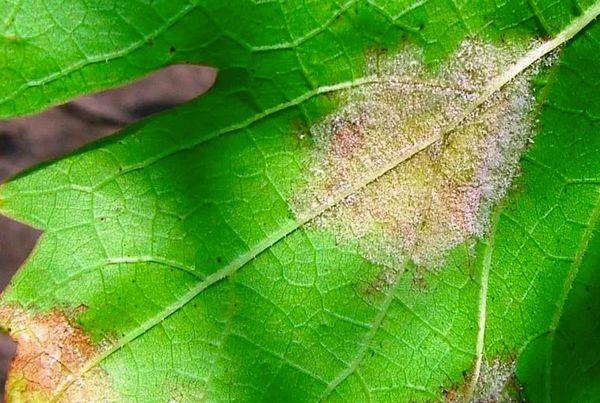

Oidium
White spots with a powdery coating appear on buds and shoots, and a grayish, web-like coating appears on leaf blades. To save the bushes, they should be sprayed with colloidal sulfur (3-6 times at intervals of 1.5-3 weeks). Switch and Karatan can be used to prevent the disease.
Gray rot
The fungus attacks one-year-old wood, leaves, inflorescences, and fruits. A coating and brown lesions are visible on them. Preventative measures include using Bordeaux mixture at two-week intervals. Treat the bushes with Ronilan (0.1%) and Rovral (0.75%).
Bacterial cancer
The disease can be identified by swelling of the bark and light-colored growths on the bushes. Treatment of grapes involves the use of 5% copper sulfate or 5% naphthenate.
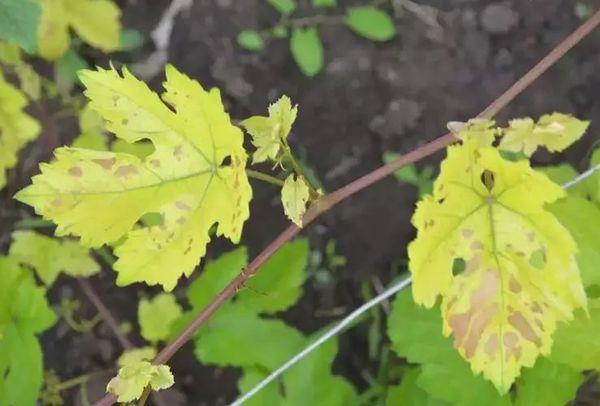
Chlorosis
The leaves lose their green color and turn yellow, and the bush stunts. Copper sulfate is used as a preventative measure, and fungicides are used for treatment.

Leaf roller
Tokution, Sumicidin, and Cymbush solutions are effective in controlling the pest. Cidial, Sevin, and Parathion are also effective.
Phylloxera
To destroy the pest, the bushes are treated with DI-68, Danadim, BI-58, Fufanon.
Ticks
If Victoria grapes are attacked by mites, use a solution based on Kelthane or Fozalon.
Mole crickets
Karbofos and benzophosphate are effective against the parasite. The solution is applied to the soil around the grapevine's trunk.

May beetles
Pest larvae and adults must be collected from bushes by hand. They are then destroyed.
Wasps
Given the sweetness and juiciness of Victoria grapes, they are often attacked by wasps. Mesh bags and special traps placed near the bushes can help.
Pros and cons of the variety
The advantages of the Victoria grape variety include:
- frost resistance;
- large-fruited;
- early maturity;
- increased immunity to diseases;
- good rooting.

One of the disadvantages of this grape is its tendency to crack.
Harvesting and storage
Victoria grapes are harvested in the second half of August and stored in a cool place, such as the refrigerator.
Scope of application
Since the Victoria variety is a table grape, the fruits can be used both fresh and in desserts. They are delicious. grape jams, juices, wine.

Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
To ensure that Victoria grape bushes grow and develop quickly and produce a rich harvest, it is necessary to:
- purchase high-quality seedlings;
- plant in a well-lit area;
- do not ignore preventive measures;
- do not overdo it with watering;
- apply fertilizer periodically.
Victoria grapes are a presentable and promising variety. With proper care, they produce consistently fruitful crops. They adapt quickly to new conditions, and reviews are generally positive.











