- History of selection of the Aport variety
- Characteristics and features of the apple tree
- Growing area
- Lifespan of a tree
- Tree dimensions
- Pollinator varieties
- Features of ripening and fruiting
- Productivity
- Winter hardiness and disease resistance
- Pros and cons: is it worth planting in your garden?
- Planting and care
- Site selection and preparation
- Layout
- Timing and technology of planting seedlings
- We organize watering and fertilizing
- Loosening and caring for the tree trunk circle
- Seasonal treatments
- Do I need to cover it for the winter?
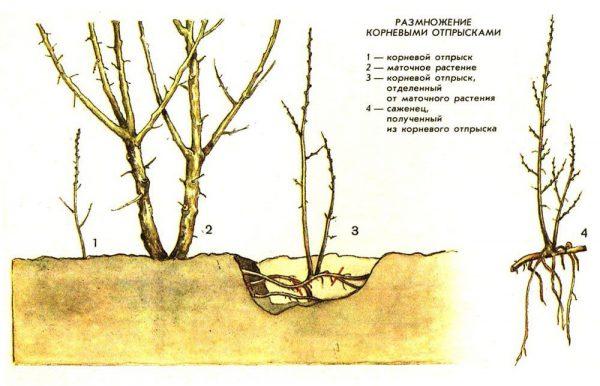
- Reproduction of culture
- Varieties of the variety
- Almaty
- Blood red
- Alexander
Apples are not only delicious but also healthy. Breeders have developed numerous varieties of this crop. Many of them trace their origins to the Aport apple tree, first mentioned in the 12th century. Below is information on the characteristics and features of this crop, its advantages and disadvantages, planting, care, propagation, and the various varieties.
History of selection of the Aport variety
The Aport apple tree is an ancient variety, known since the 12th century. Some sources believe its origin is Turkey, others Italy, and still others the territory now occupied by Ukraine. In the 19th century, the variety consistently won prizes at various exhibitions, positioning itself as a Russian variety. Its hardiness in mountainous conditions earned it the status of a symbol of the Issyk-Kul region.
Characteristics and features of the apple tree
Many apple varieties are characterized by periodic fruiting. Aport is one such variety. The tree produces fruit once every two years.
Growing area
Since this variety doesn't tolerate frost well, it's mainly grown in warmer regions. In northern regions, it can be grown by planting it at a 45° angle and bending the stems to the ground in winter. Grafting Aport onto frost-resistant varieties will also help.

Lifespan of a tree
An apple tree can grow and bear fruit for 40 years. With proper care and pruning of drooping shoots, the tree's lifespan is extended.
Aport lovers can propagate this planting by seeds or by grafting it onto a wild apple tree.
Tree dimensions
The average tree height is 5-6 meters. This apple tree has a spreading habit, with a crown diameter of approximately 10 meters. The long shoots are of medium thickness. Green leaves are located at the ends of small branches.
Pollinator varieties
The Aport apple tree can bear fruit without pollinators, but the yield will be higher if pollinators are planted nearby. The most suitable varieties for this tree are Prikubanskoye, Pamyat Esaulya, and Shchit. They guarantee a large number of apples on the trees.
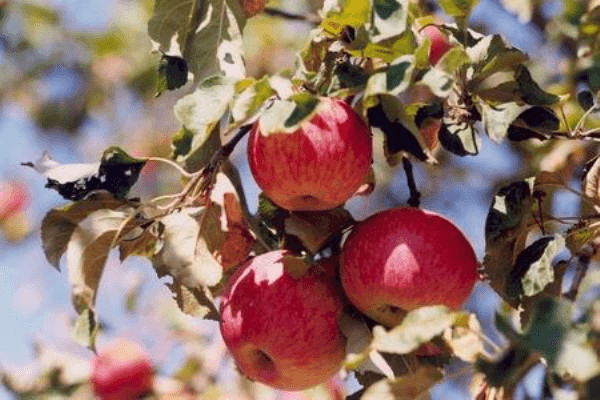

Features of ripening and fruiting
Ripening times depend on the planting region and weather conditions. In warmer regions, flowering begins in early May, and the fruit can be harvested in September. The Aport apple tree's fruiting period is characterized by fruiting occurring in the 7th to 8th year of growth, occurring every two years.
Productivity
The red-yellow fruits of the Aport tree weigh an average of 250-270 grams. An average mature tree can yield 150 kilograms of apples. If the yield decreases, it's necessary to reconsider the amount of fertilizer applied. Excessive nitrogen reduces the development of green mass at the expense of fruiting.
Winter hardiness and disease resistance
The variety doesn't tolerate cold winters well, so it's often grafted onto more frost-hardy apple varieties. Aport is susceptible to diseases common to the cultivar. To avoid these, preventative measures are necessary: spray the trees with antifungal agents several times a season and remove weeds and fallen leaves.
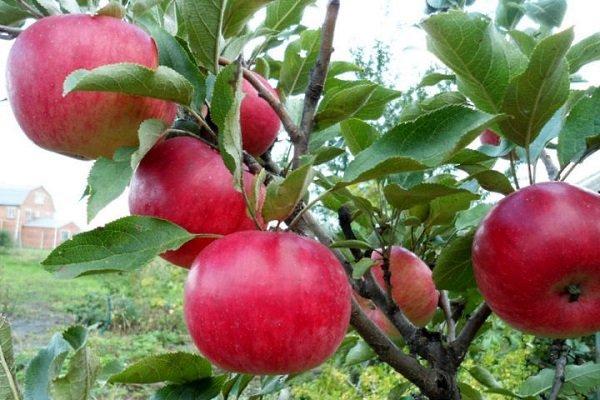

Pros and cons: is it worth planting in your garden?
The advantages of the variety include the following qualities:
- large fruits;
- good taste and aroma of fruits;
- transportability occurs without losses;
- excellent presentation of apples;
- the possibility of using fruits in cooking.
The disadvantages include the following characteristics:
- fruiting occurs once every 2 years;
- poor frost resistance;
- susceptibility to various diseases.
Despite some drawbacks, the Aport apple variety has many more advantages. When grafted onto a stable rootstock and given proper care, the tree will display all its positive qualities.
 Tip! Since the Aport apple tree is a spreading variety, it's best to plant it at least 5 meters away from buildings.
Tip! Since the Aport apple tree is a spreading variety, it's best to plant it at least 5 meters away from buildings.
Planting and care
Choosing the right time and location for planting an apple tree is crucial. To ensure the tree thrives, it requires careful care throughout the season: watering, fertilizing, and preventative spraying against diseases and pests. Additionally, the crown should be periodically thinned to ensure the apples receive sufficient sunlight.
Site selection and preparation
Choose a well-lit, wind-protected site for planting the seedling. Loamy soil enriched with compost and peat moss is best. If the groundwater level is more than 1 meter above the soil surface, dig drainage pits near the tree to drain excess water.

Layout
It's recommended to prepare the planting hole six months before planting the apple tree. To do this, dig a hole 1 meter deep and 1 meter in diameter. Mix garden soil with compost, sand, and wood ash. If you plan to plant several trees, keep in mind that the crown of a mature tree can extend up to 10 meters.
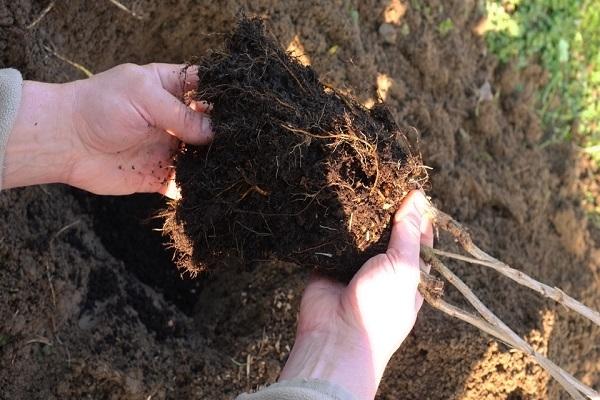
Timing and technology of planting seedlings
The Aport apple tree is planted in spring or fall. Planting is done as follows:
- a mound is made in a hole prepared in advance;
- the apple tree root system is distributed along it;
- the space around the roots is filled with soil;
- The top layer is lightly compacted and watered.
The root circle is sprinkled with compost or peat from above.

We organize watering and fertilizing
To ensure the seedling takes root, it needs to be watered frequently. Subsequent watering depends on weather conditions: if the summer is dry, the soil should be moistened once every two weeks. Watering is especially important from budding until the fruit is fully ripe.
Fertilizing of the apple tree begins in the 3rd year after planting.
For this purpose, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are used in the spring, and those containing primarily potassium and phosphorus are used before and after flowering. Another fertilizer application is made in the fall to help the tree survive the winter more easily.
Loosening and caring for the tree trunk circle
To ensure adequate airflow to the roots, the soil around the tree trunk should be loosened. To conserve moisture, mulch it with humus or peat. Weeds that form around the plant should be removed, otherwise they will rob the plant of nutrients and light.

Seasonal treatments
To reduce the risk of disease and pests, trees should be sprayed with chemicals several times per season. The first treatment is done before bud break, the next before flowering. A third spray is applied when the petals fall, and another two weeks later.
Do I need to cover it for the winter?
The Aport apple tree isn't known for its frost resistance, so it's usually grafted onto winter-hardy rootstocks. In northern regions, it's planted at an angle to protect the shoots from frost during the winter. When cold weather sets in, the root zone is covered with compost and dried leaves.
Reproduction of culture
Apple trees can be propagated in several ways: by seeds, cuttings, layering, and grafting. Gardeners generally don't use seed propagation because it's labor-intensive, and such trees tend to bear fruit late. The most common method for propagating a cultivar is grafting onto a wild apple tree.
Varieties of the variety
Aport has several clone varieties. They have roughly the same characteristics, but some differences do appear.
Almaty
This cultivar was developed by Kazakh breeders. It is adapted to growth and fruiting in mountainous conditions. The Almaty apple variety produces large fruits that can be stored until the following summer.
Blood red
The apple tree gets its name from its bright red fruits. Each fruit weighs 240-260 grams, and its flesh is creamy and has a spicy flavor. The fruits ripen in late September or early October.
Alexander
This variety is almost a perfect copy of the Aport. The only difference is that the Alexander has more prominent light stripes. Furthermore, its flesh is more yellow.











