- Selection and cultivation area of the Arbat apple tree
- Advantages and disadvantages of columnar varieties
- Botanical description
- Size and annual growth
- Crown and branches
- Foliage and buds
- Fruiting of the tree
- Flowering and pollinators
- Ripening time and yield per tree
- Harvesting and storage
- Fruit tasting and the scope of apple trees
- Resistance to adverse climatic conditions
- Susceptibility to diseases and pests
- Planting a tree on a plot
- Required soil composition
- Selecting and preparing a landing site
- Dimensions and depth of the planting hole
- Timing and step-by-step algorithm for planting a seedling
- How to care for the Arbat apple tree
- Regularity of watering
- We apply fertilizers
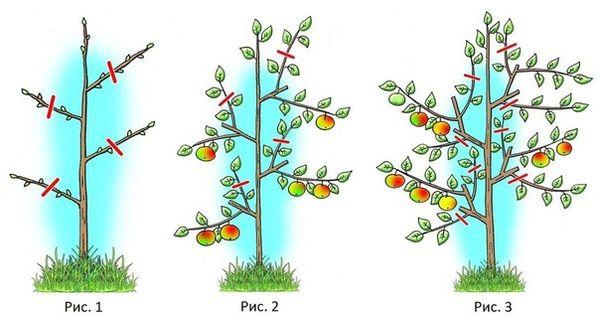
- We trim and shape the crown
- Loosening and mulching the tree trunk circle
- Prevention and protection of wood
- Covering a fruit tree for the winter
- Methods of reproduction
- Gardeners' reviews of the Arbat variety
The late-ripening columnar apple tree variety Arbat has long been known to gardeners. This compact tree produces its first harvest within a year of planting. The lack of a broad crown and side branches allows for several neat fruit-bearing beauties to be planted in a plot. This variety is winter-hardy, but it is recommended to cover the tree for the winter.
Selection and cultivation area of the Arbat apple tree
The columnar apple variety Arbat was bred in Moscow. It was developed in 1984 by V.V. Kichin by crossing two varietal forms: a columnar form donor with a scab immunity donor. This variety is primarily grown in the southern regions of our country. When grown in temperate continental climates, it requires additional winter protection.
Advantages and disadvantages of columnar varieties
Gardeners speak highly of the columnar Arbat apple tree variety. Its key advantages include:
- compactness of the tree;
- abundant regular fruiting;
- strong immunity to scab and various types of fungal diseases;
- decorative qualities;
- winter hardiness.
The following are some of the variety's disadvantages:
- ripe fruits are stored for no more than three weeks;
- average transportability of apples;
- the lifespan of a tree is about 15 years;
- Over time, the fruits become smaller.
The lifespan of a tree can be increased by proper systematic pruning, which begins in the 5th year of life.
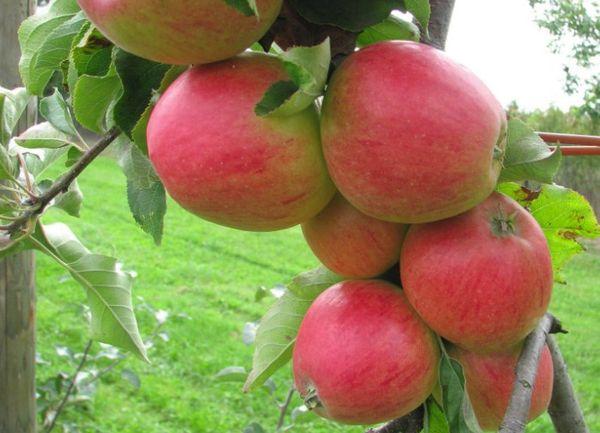 Important! Arbat produces excessive fruit, unevenly distributed throughout the tree; the apple tree is prone to overload. Excess fruit should be removed from the tree in advance.
Important! Arbat produces excessive fruit, unevenly distributed throughout the tree; the apple tree is prone to overload. Excess fruit should be removed from the tree in advance.
Botanical description
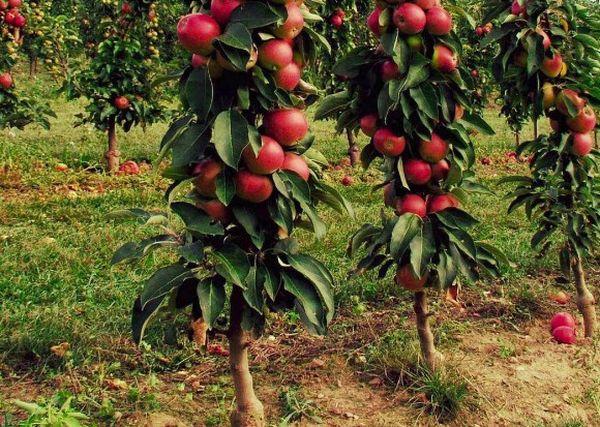
The tree's lack of a crown and compact shape allow it to be grown in a space of 0.5 square meters. Six seedlings of this columnar variety can replace one full-sized mature apple tree.
Size and annual growth
The Arbat tree is characterized by a slow growth rate. A mature plant reaches 3-4 meters. However, the tree does not grow in diameter, does not develop lateral branches, and the fruit is attached directly to the trunk.
Crown and branches
Columnar apple trees lack a crown in the traditional sense. The tree's shape is pyramidal. There are no lateral branches. The trunk is dense, covered with leaves and fruit.
Foliage and buds
The leaves are attached to the tree's trunk. The leaf blades are elongated, with small serrations on the edges. The fruits ripen on the trunk, reminiscent of a Christmas garland. The apples are easy to pick.
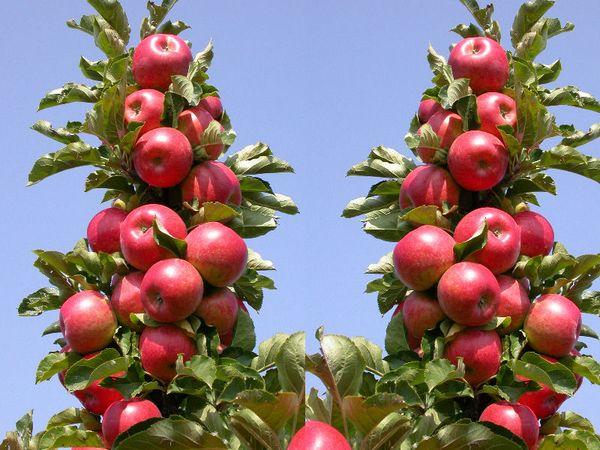

Fruiting of the tree
The first fruits of the Arbat tree can be enjoyed a year after planting. The tree reaches its peak yield in its sixth year.
Arbat is a late-ripening summer variety; ripe apples are harvested in late August – early September.
Flowering and pollinators
Buds form on shortened growth. The tree begins blooming in mid-May, with pale pink petals. Arbat is a self-fertile columnar apple variety, but the presence of pollinators doubles fruit set. The Ostankino and Teleimon varieties are used as pollinators.
Ripening time and yield per tree
The yield per tree is 20 kilograms, with the maximum fruit yield occurring in the sixth year after planting. Over time, the fruits begin to become smaller. Harvesting can begin in late August.
Harvesting and storage
Arbat's transportability is poor. Freshly picked fruits have a shelf life of no more than one month.
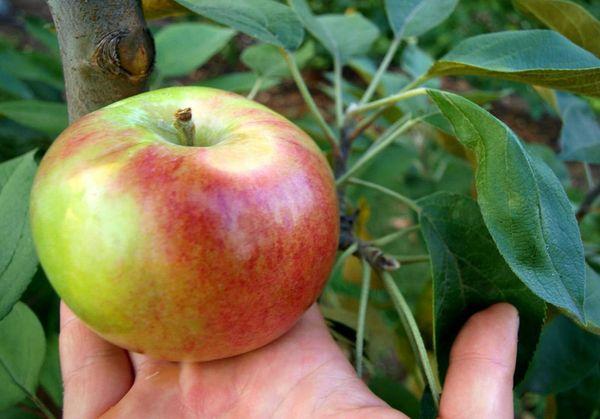

Fruit tasting and the scope of apple trees
Apples are versatile. They have a sweet and sour flavor, are juicy, have firm flesh, and a distinct apple aroma. They are best eaten fresh, processed into juice, applesauce, and jam.
Resistance to adverse climatic conditions
Arbat is distinguished by its high winter hardiness for columnar varieties, and is able to withstand winter frosts down to -30 C. Cool summers do not reduce yields. Drought resistance is good.
Susceptibility to diseases and pests
The variety is resistant to scab and fungal diseases. It is important to treat the trees with fungicides in the spring to prevent insect infestations. Before flowering, spray the trees with Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate.
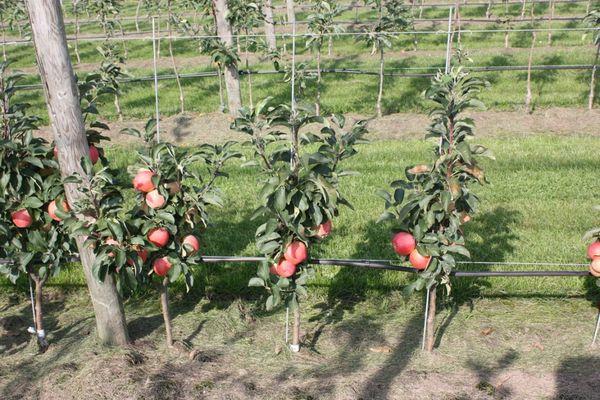

Planting a tree on a plot
Instead of one standard apple tree, you can plant six columnar varieties on your plot. Arbat has no special soil requirements, but it's important to prevent moisture stagnation at the plant's roots.
Required soil composition
Apple trees grow most successfully in light, fertile soils. It is recommended to install drainage at the bottom of the planting hole. The soil should be neutral in pH, and organic fertilizers should be added directly to the planting hole.
Selecting and preparing a landing site
The site for planting columnar apple trees is selected in advance. A south-facing location, free from drafts and shade, is preferred. Apple trees grow poorly in lowlands and marshy soils, and yields are reduced.
Dense planting is practiced, with a distance of 40 centimeters between seedlings. It is important to maintain a checkerboard pattern to ensure proper distribution of light for the trees.

Dimensions and depth of the planting hole
The planting hole should be 0.5 meters deep and 0.5 meters in diameter. Fill the hole with humus, wood ash, and superphosphate. The distance between seedlings depends on the chosen planting method.
Timing and step-by-step algorithm for planting a seedling
Drainage with expanded clay and sand should be installed in the prepared holes. Organic fertilizer, compost mixed with wood ash, and two handfuls of urea are added. A small mound of the resulting mixture is made in the center of the hole, and the roots are carefully spread out on it. The plant is covered with soil, watered, the soil is compacted, and the area around the trunk is mulched.
How to care for the Arbat apple tree
The care system for a columnar apple tree consists of watering, fertilizing, and properly shaping the fruit load on the plant's trunk.
Arbat needs winter shelter and preventative spraying with fungicides against insect pests.
Regularity of watering
Arbat requires additional watering only during prolonged droughts. Excess moisture at the plant's roots can lead to fungal infections and slow growth.

We apply fertilizers
The first fertilizing begins the following year after planting. Use ammonium nitrate, mullein, bird droppings infusion, and mulching the tree trunk area with humus. Potassium-phosphorus complexes and calcium are important for apple trees during the flowering and budding period.
We trim and shape the crown
The Arbat tree's crown is narrow and easy to care for. It's important to promptly remove dry branches and lateral shoots, which form extremely rarely.
Loosening and mulching the tree trunk circle
The tree trunk area requires regular maintenance. The soil should be loosened to a depth of 5-8 centimeters, weeded, and covered with a mixture of sand and humus. For group plantings, use agrofibre or fill the area around the tree trunk with mown grass.

Prevention and protection of wood
The following measures are taken as preventative measures against insect pests and fungal infections:
- Whitewashing of tree trunks with lime.
- Sanitary pruning of the crown.
- Spraying trees with Bordeaux mixture in spring and autumn.
- Planting fragrant plants next to fruit trees: coriander, marigolds, calendula.
- Regularly clear the tree trunk circle of weeds.
Arbat is distinguished by its strong immunity to scab.
Covering a fruit tree for the winter
The Arbat tree requires additional winter protection, as the treetop may freeze. The area around the trunk is carefully loosened, weeds are removed, and mulched with last year's leaves. The trunk is covered with spruce branches or special agrofibre.
Methods of reproduction
Propagating a columnar apple tree on your own is difficult; only experienced gardeners can do this. The primary method of propagation is grafting. Beginners are advised to purchase Arbat seedlings from specialized stores and nurseries.
Gardeners' reviews of the Arbat variety
Anastasia Yuryevna Strelnikova, 64, Kazan: "I've dreamed of an orchard my whole life. We recently purchased a small plot of land, just 600 square meters, where we needed to add a sauna and a vegetable garden. Space was critically limited. My husband and I decided to try planting the columnar Arbat apple variety.
At first, we couldn't believe such small apple trees—we planted three of them side by side—could produce a substantial harvest. Four years later, Arbat surprised us. We harvested three buckets of apples from one fragile tree! A success! I recommend this variety to any gardener with a small plot dreaming of an orchard.











