- The history of the Solnyshko apple tree breeding
- Description and characteristics
- Tree size and annual growth
- Branching of the root system
- All about fruiting
- Flowering and pollinators
- Ripening time and harvest
- Yield and tasting qualities
- Scope of apples
- Susceptibility to diseases and parasites
- Frost and drought resistance
- Planting technology
- Deadlines
- Keep your distance
- Preparing seedlings and planting
- Specifics of care
- Watering and fertilizing
- Loosening and mulching the soil
- Trimming
- Insect and disease prevention
- Covering a tree for the winter
- Subspecies and variants
- Dwarf and semi-dwarf
- Columnar
- Orlovskoye
- Peculiarities of cultivating the variety in different regions
- In the Moscow region
- In the Leningrad region
- In the Urals
- Methods of reproduction
- Reviews
In the early 2000s, the Solnyshko apple variety became popular among gardeners and farmers. Although a relatively recent development, it is already being used for commercial production. These apples boast excellent breeding properties, including frost resistance and resistance to common diseases. The plant requires controlled soil moisture.
The history of the Solnyshko apple tree breeding
The Solnyshko apple variety was developed at the end of the last century at the All-Russian Research Institute of Fruit Crop Breeding. The breeding work was carried out by a group of Russian scientists led by Academician E. N. Sedov. They succeeded in developing a winter-hardy apple variety with robust immunity to scab.
The Solnyshko variety is considered an elite variety due to its superior qualities. It is recommended for cultivation in the Central, Central Black Earth, and Lower Volga regions.
Description and characteristics
Solnyshko is a winter-hardy, high-yielding late-autumn variety with unique characteristics:
- the trees are squat and low;
- the crown is sparse and rounded;
- trunk with burgundy-brown glossy bark;
- shoots are thick, curved in an arc, geniculate;
- leaves are oval with a sharp twisted tip, slightly shiny, serrated;
- flowers are pinkish-white, collected in inflorescences of 4-6 pieces;
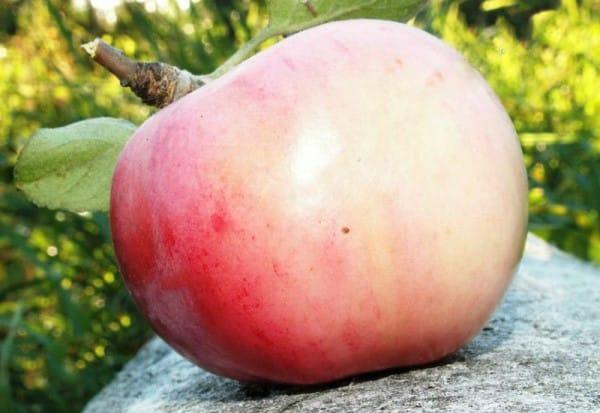
- the fruits are small, oblong (average weight 140 grams);
- the apple skin is dense, smooth, light yellow, with noticeable subcutaneous dots;
- the cup is closed, with a shallow conical sub-cup tube;
- the peduncle is short;
- heart-shaped onion, seed chambers closed;
- seeds are light brown, elongated;
- The pulp is juicy, milky white, fine-grained.
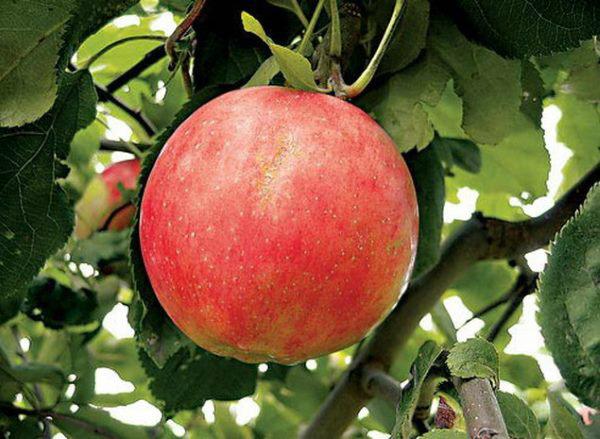

The Solnyshko apple tree lives 25-30 years, actively bearing fruit for about 15 years (from 7 to 20 years).
Tree size and annual growth
Mature trees don't grow taller than 3.5 meters, while those grown on dwarf rootstocks reach 1.5-2 meters. With proper annual pruning, average annual growth can be increased to approximately 40 centimeters, but it shouldn't be less than 15 centimeters per year.
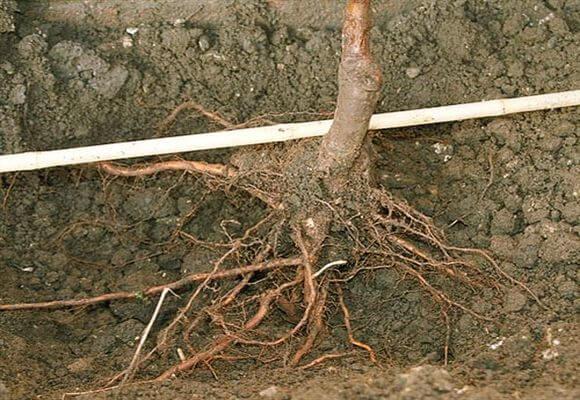
Branching of the root system
The apple tree has highly branched, fibrous roots. These continue to grow until the tree's 20th year, penetrating deep into the soil. Horizontal, invasive roots are located in the top 50-centimeter soil layer. Their spreading width is equal to the crown projection.

All about fruiting
The Solnyshko variety is distinguished by its high yield and long shelf life.
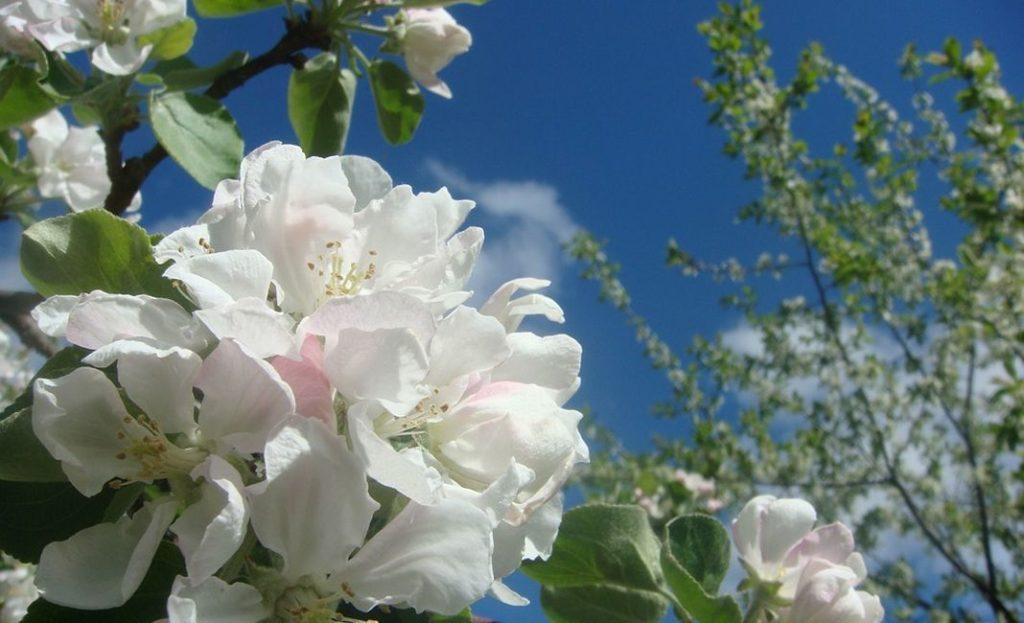
Flowering and pollinators
This apple tree is self-sterile and requires the planting of pollinators. The best pollinators are:
- Antonovka;
- Orlik;
- In Memory of the Warrior;
- Imbrus.
The tree blooms in May, during the leaf opening period, in the 2nd-3rd decade.

Ripening time and harvest
Apples ripen en masse after September 15th, reaching harvestable maturity. By early October, the fruit is fully ripe and reaches consumer quality. The shelf life is 60-90 days.
The skin is susceptible to damage, so care is required. The fruits should be picked in warm weather, carefully, stems included, and placed in a dry wooden container in a single layer.
Yield and tasting qualities
The Solnyshko variety is suitable for high-intensity orchards. Each tree produces up to 200 kilograms of fruit per season.
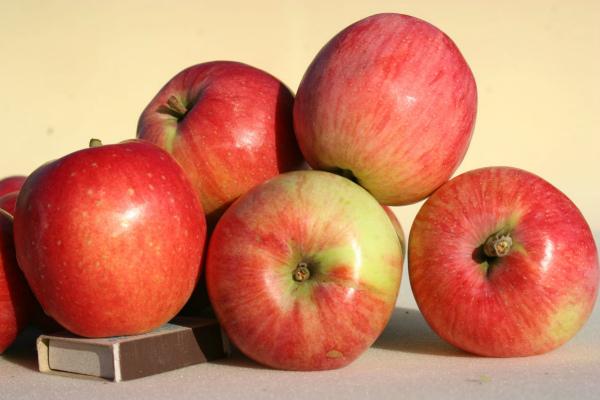

On a tasting scale with a maximum value of 5 points, Solnyshko apples have the following ratings:
- external attractiveness: 4.4 points;
- taste qualities: 4.3 points.
The fruit has a memorable sweet and sour taste and a distinct aroma.
Chemical content:
- sugar – 7.9%;
- titratable acid – 0.86%;
- ascorbic acid – 7.2 mg per 100 grams.
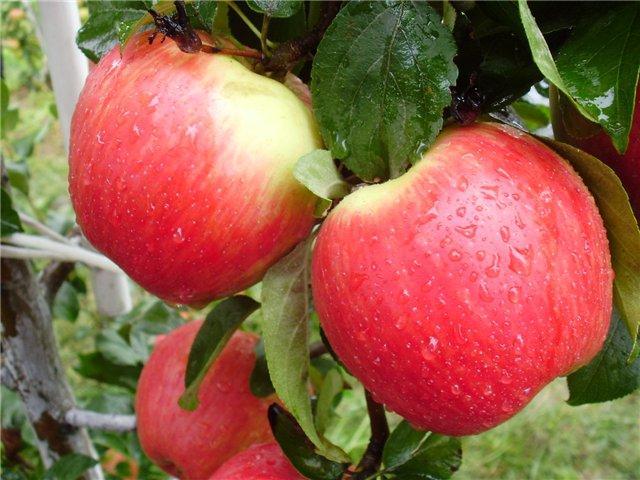

Scope of apples
Solnyshko apples have a rich flavor, contain an optimal amount of sugar, and are rich in minerals, vitamins, pectin, and organic fruit acids. The fruit can be eaten fresh or used to make jam, preserves, juice, preserves, compote, and cider.
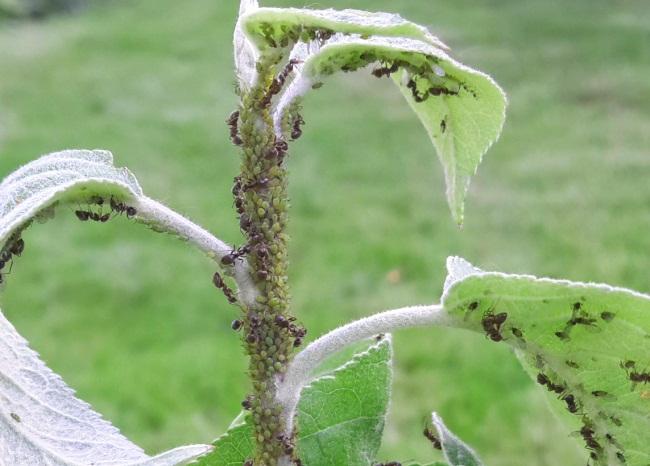
Susceptibility to diseases and parasites
The undeniable advantages of the variety include immune resistance to scab.
However, without special insecticide treatment, the plant is at risk of attack by parasites:
- codling moths;
- red tick;
- flower beetle;
- psyllids;
- copperheads;
- aphids.
Diseases that trees of this variety may be susceptible to include moniliosis, powdery mildew, and apple black cancer.

Frost and drought resistance
The Solnyshko apple tree's high winter hardiness was proven by artificial freezing tests at the Research Institute of Fruit Plant Breeding. No significant damage was observed after exposure to temperatures of -40 degrees Celsius.
The variety is relatively resistant to drought due to its deep roots.
Planting technology
Planting an orchard requires careful adherence to technology: mistakes made will be quite difficult to correct, and yields may decrease.
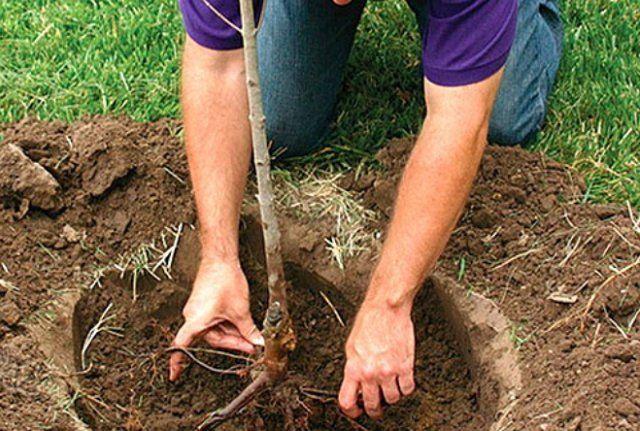

Deadlines
Seedlings are planted in the spring before the buds open or in late autumn when the leaves have fallen but there is no frost yet.
Keep your distance
It's important to leave sufficient distance between seedlings when planting. This should be at least 3 meters for dwarf varieties and about 6 meters for full-sized ones. This will prevent the trees from competing for moisture and nutrients.
Preparing seedlings and planting
1-2 year old seedlings are freed from excess, too long or diseased roots, soaked in water or coated with wet clay.
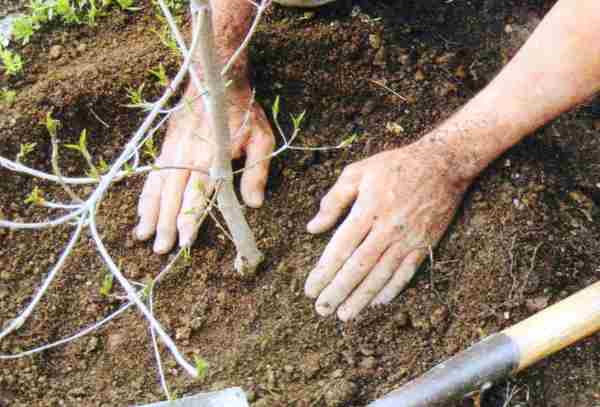

Holes approximately 1 m in diameter are prepared in advance, approximately 10-14 days before planting. The bottom is filled with drainage material, and a mound is made in the center. The seedling is placed on top, carefully spreading the roots along the edges.
Then fill the hole with a mixture of soil, humus, sand, fertilizers, and compact it, having first installed a support.
The hole containing the seedling of this variety is watered generously with warm water, as much as the soil will absorb. After the soil settles, add more and compact it again.
Specifics of care
The Solnyshko apple tree is unpretentious in care, but requires regularity in standard procedures.

Watering and fertilizing
This variety doesn't require abundant watering: moderate but frequent moistening is preferred. Excess moisture can damage the tree, so it's recommended to create drainage channels during periods of heavy rainfall.
Every year, before fruit formation and growth, mineral fertilizers (magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus) should be added. Organic fertilizer is applied under the trunk in the spring during soil loosening.
Loosening and mulching the soil
Loosen the soil to improve oxygen and nutrient availability to the roots. Mulching helps control weeds, which are especially harmful to young seedlings.

Trimming
Pruning of trees of this variety is carried out in the spring, removing all damaged, dry, diseased, inward-growing and vertical branches.
Insect and disease prevention
Diseases and insect pests must be controlled regularly. It's important to monitor the condition of plants and take immediate action before the infestation spreads to neighboring trees.

Covering a tree for the winter
This variety does not require winter cover when grown in the recommended regions, as it is frost-resistant.
Subspecies and variants
There are several subspecies of the Solnyshka apple tree, which have minor differences.
Dwarf and semi-dwarf
Dwarf and semi-dwarf apple trees are produced by grafting onto dwarf rootstocks. They begin bearing fruit at 3-4 years of age and do not exceed 2 meters in height.

Columnar
Columnar apple trees have a more compact crown, allowing for more frequent plantings and higher yields per hectare. However, the Solnyshko apple variety does not have such a subtype.
Orlovskoye
Orlov apple varieties are those with a distinctive genetic resistance to scab, developed by scientists at the All-Russian Research Institute of Selective Fruit Crops. Therefore, there is no separate Orlov subspecies of the Solnyshko apple tree. They are all the same variety.

Peculiarities of cultivating the variety in different regions
The Solnyshko variety has potential for cultivation in central Russia, including on an industrial scale.
In the Moscow region
In the Moscow region, apple trees are grown according to general recommendations. This region is suitable for growing this variety.
In the Leningrad region
The Leningrad Region is characterized by high average annual humidity and heavy rainfall. Water drainage will be required for trees of this variety.

In the Urals
The Solnyshko variety is not officially zoned for the Urals. Presumably, growing this variety in the Urals region will not pose any particular problems.
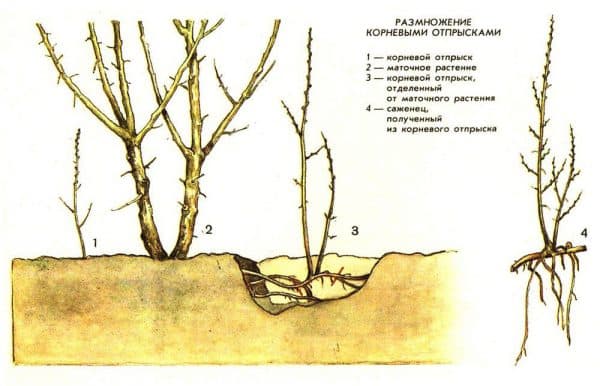
Methods of reproduction
Propagation by seedlings is the simplest and only acceptable method of propagation, since other methods are unnecessarily complex and do not guarantee results.
Reviews
Sergey Vladimirovich, Chekhov:
"The harvest is fully ripe by mid-September. The apples are very tasty, especially when fresh from the tree, but they drop a lot. The tree has never had scab."
Galina, Moscow:
"Very beautiful fruits, excellent taste. But the apple tree died from cytosporosis. Copper-containing preparations did not help save the tree."
Victor Bratkin, Ryazan
"The fruits are quite large, which is probably why some fall off long before they're ripe. On seedling rootstock, it's difficult to control the tree's growth; a lot of pruning is required."











