- The main causes of cabbage diseases
- Diseases characteristic of the culture and methods of combating them
- Slimy bacteriosis or black rot
- Kila
- Phoma - dry rot
- Downy mildew
- Sclerotinia - white rot
- Botrytis - gray mold
- Alternaria - black spot
- Fusarium
- Mosaic virus
- Blackleg
- What pests are dangerous for cabbage: ways to get rid of parasites
- Cabbage moth
- Cabbage moth
- Cabbage white butterfly
- Cabbage fly
- Cabbage aphid
- Rape sawfly
- Cruciferous bug
- Cruciferous flea beetle
- Whitefly
- Slugs
- Prevention of diseases and pest infestations
- Timely preventive treatments
- Proper care of the plant
Cabbage is a popular vegetable among Russian gardeners. This plant boasts a pleasant flavor and beneficial micronutrients. However, not every variety is disease-resistant. Vegetable growers and cabbage lovers need to treat and manage any diseases promptly. Only then will they be able to reap a bountiful harvest.
The main causes of cabbage diseases
The main causes of cabbage diseases include the following factors:
- excessive soil moisture;
- high soil acidity;
- the presence of fungal microorganisms in the soil;
- dense planting of seedlings;
- oversaturation of soil with nitrogen;
- temperature not exceeding 18 degrees;
- prolonged lack of moisture;
- storing cabbage in a damp place;
- storing cabbage in conditions of elevated temperatures.
Diseases characteristic of the culture and methods of combating them
Plant diseases can deprive a gardener of their harvest. To avoid this, it's important to understand the main signs of disease, how to combat them, and how to take preventative measures.
If the fight against the disease is started in a timely manner, it will be possible to save the crop.
Slimy bacteriosis or black rot
Black rot can affect the outer leaves. They become deformed and develop an unpleasant odor. After a certain period, the rot spreads to the head, and the plant slowly dies.
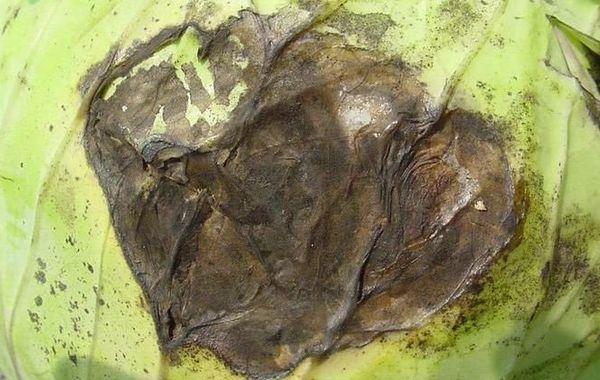
Slimy bacteriosis can also affect the cabbage stalk. Microbes enter the cabbage from the soil or are carried by pests. Black rot then spreads to the inner leaves, causing them to change color and become soft.
To prevent mucous bacteriosis, the following conditions must be observed:
- proper storage of crops;
- constant fight against harmful insects;
- growing plants resistant to black rot;
- disinfection of seedlings before planting;
- treatment of the place where the harvest will be stored.
Kila
The disease develops in the root cells of cabbage plants. Clubroot typically affects seedlings. Growths appear in the root system, disrupting the plant's nutrition. This can prevent fruit buds from forming. At the end of the growing season, the root growths rot, decompose, and penetrate the soil, which becomes contaminated.

Fighting the disease is quite simple; the key is to detect it early. Dead or wilted cabbage should be removed from the garden along with the soil. The planting site should be sprinkled with lime.
It is not recommended to plant seedlings infected with clubroot in order to increase the yield. However, other plants can be planted in infected soil, as clubroot only affects cruciferous plants.
Phoma - dry rot
Black spot affects the leaves, stems, and roots of cabbage. Gray or discolored spots with dark spots form on them. The cabbage turns yellow, and head development is stunted. Black spot can be introduced through infected seeds or plant debris. To control it, you need to:
- observe crop rotation;
- plant seedlings in accordance with planting deadlines;
- apply fertilizers;
- how to properly care for cabbage;
- make sure that the seeds are not affected by phomosis;
- destroy plant remains;
- carry out processing;
- maintain storage conditions suitable for cabbage heads;
- select the stalks before planting.
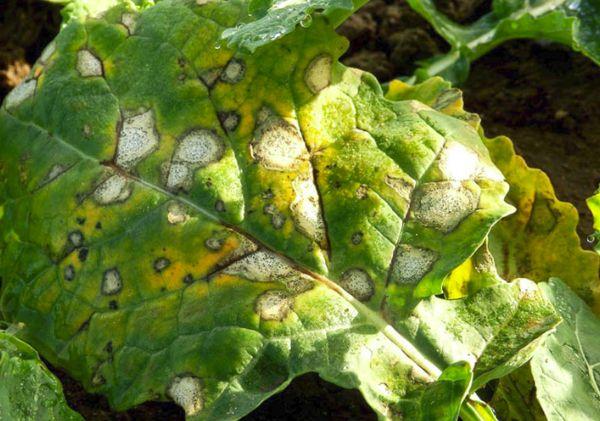

Downy mildew
Active downy mildew development occurs when temperatures exceed 20 degrees Celsius. When seedlings are planted in raised beds, downy mildew progresses more slowly.
The first signs of the disease appear with the onset of warm weather. Light-colored leaves and their veins become scabby. Red spots also appear on them. Plants affected by downy mildew gradually wither.
There are no effective ways to get rid of downy mildew. Control involves promptly treating plants and creating optimal conditions for plant growth.
As a preventative measure, it's recommended to treat the seeds before planting. Place the seeds in heated water for 30 minutes, then treat with Planriz.
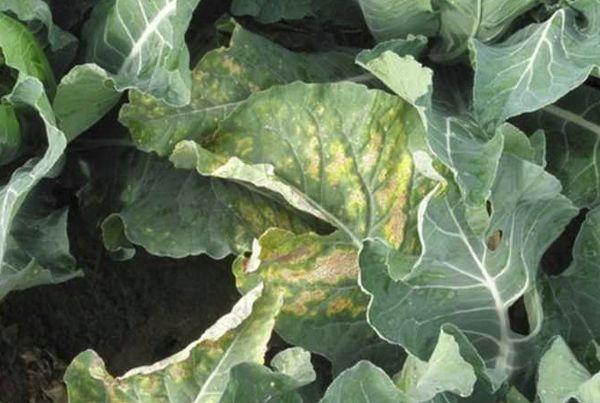
Sclerotinia - white rot
Sclerotinia thrives in humid conditions, so be sure to maintain optimal humidity. Also, do the following:
- calcine the soil before planting;
- use fertilizers (1 gram of zinc sulfate, 2 grams of copper sulfate, 10 grams of urea, 10 liters of water);
- Observe storage conditions.

Botrytis - gray mold
Rules for combating gray mold:
- watering the bushes with heated, settled water;
- failure to use nitrogen fertilizers;
- timely collection of cabbage heads;
- wiping the fruits dry before storing;
- storing fruits at a temperature of 3-4 degrees.
Alternaria - black spot
To combat black spot, follow these rules:
- destroy plant debris;
- use pest control products;
- Dry seeds thoroughly before planting.
Fusarium
Fusarium wilt is incurable, so there are no effective treatments. The only option is to remove all affected plants. Alternatively, you can treat the plants with copper sulfate.
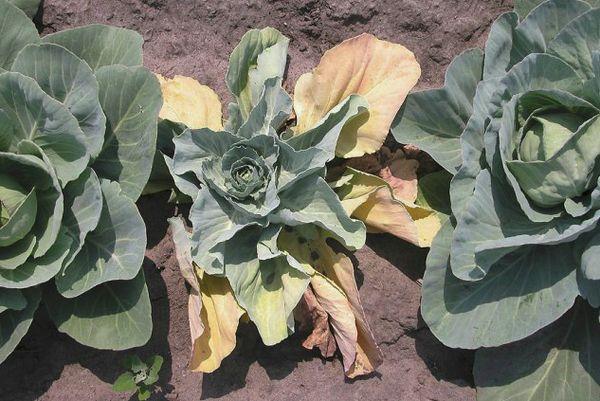

Mosaic virus
Treating the affected cabbage will be ineffective, as mosaic disease is incurable. Preventative measures include promptly removing weeds from the garden and controlling pests.
Blackleg
To combat black leg in the phase of 2-3 cabbage leaves, spray with a solution of Fitosporin-M (0.2 percent, 1.4-1.5 kilograms per hectare).
What pests are dangerous for cabbage: ways to get rid of parasites
Cabbage and other cruciferous plants are subject to pest attacks throughout the growing season, but insects pose the greatest danger in the early stages of bush formation.
Cabbage moth
To combat cabbage moth, you need to:
- carry out autumn tillage;
- destroy weeds;
- use biological and insecticidal preparations.
Cabbage moth
If cabbage is attacked by the cabbage moth, biological control agents are required. Both Dendrobacillin (2 kilograms per hectare) and Lepidocide (1 kilogram per hectare) can be used.

Cabbage white butterfly
Protecting cabbage grown outdoors from cabbage whites can be done using the same methods as moth control. Dendrobacillin and Lepidocide are the best protection for all cruciferous plants against cabbage whites.
Cabbage fly
The following is effective against cabbage flies:
- Be sure to remove stalks and other plant debris from the beds. Carry out autumn cultivation;
- exclude radishes from the crop rotation, which attract pests;
- carry out chemical immunization of bushes after planting (macro- and microfertilizers);
- when pests lay their eggs en masse, apply Diazinon granules under the bushes (30-40 kilograms per hectare);
- During the summer, spray the bushes with fifty percent Karbofos to kill pests.
Cabbage aphid
To get rid of aphids, prepare a 2% solution of anabizin sulfate. Apply half a liter of the solution for every 10 square meters.
If chemicals are unavailable, use a tobacco infusion. Soak 400 grams of tobacco leaves in 2 liters of water for a couple of hours. Then, when the infusion has cooled, strain the leaves. Pour the infusion into a bucket of water and mix with 50 grams of soap. Then begin treating the bushes.
Rape sawfly
To get rid of the rapeseed sawfly:
- destroy weeds in the beds and around the perimeter of the garden;
- Crop rotation is practiced. Growing cabbage in the same place twice is not recommended;
- They dig the ground deeply in the autumn or spring season to destroy the cocoons with pupae;
- Bait plots with cabbage are planted. The bait bushes are mowed down and burned along with the sawflies that have migrated to them;
- destroy the remains of plants after the harvesting of heads of cabbage is completed.
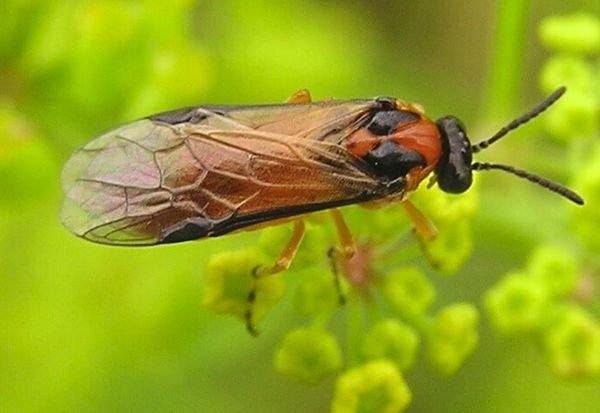

Cruciferous bug
To get rid of cruciferous bugs, you need to remember the following:
- The enemies of the bug are considered to be the trissolcus and the variegated phasia, which attack the pest.
- Practice crop rotation and use mixed plantings.
- Use electric traps, which are sold at gardening stores. The traps attract the bugs with ultraviolet light. When the bug approaches the trap, it receives an electric shock, which kills it.
Cruciferous flea beetle
To protect cabbage bushes from flea beetles, it's important to remember that planting seedlings early will only be beneficial, as by the time the pests begin to show activity, the bushes will be older and stronger than those planted late.
It is possible to increase plant resistance to cruciferous flea beetles by using fertilizers that include slurry and saltpeter additives.
Whitefly
Insecticides are used to control whiteflies. When using them, protective equipment is required: a respirator, goggles, gloves, and protective clothing.
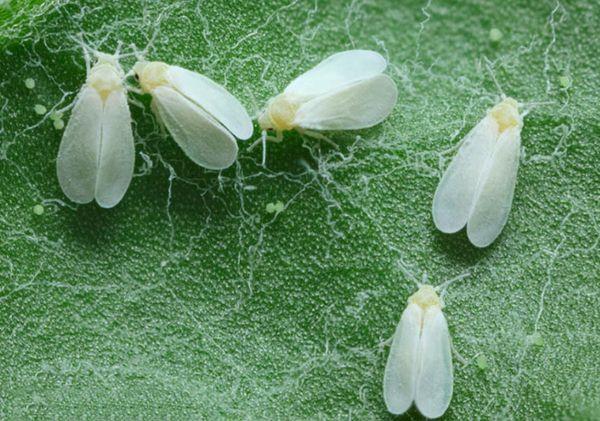

List of insecticides effective against whiteflies:
- Actellic";
- Verticillin G;
- Confidor;
- Mospilan;
- Pegasus;
- Fufanon;
- Fosbecid.
Slugs
If you don't know, How to get rid of slugs on cabbage plants To protect your crops, you should spray them. There are several popular ways to spray your bushes against slugs:
- Make strong coffee. To completely eliminate slugs, spray each plant with 2 cups of coffee.
- Use an ammonia solution. You'll need 1 part ammonia to 6 parts water. This solution will repel slugs but won't harm the plants.
- Use a weak salt solution. Don't overuse this method, as it can cause the plants to dry out.
Prevention of diseases and pest infestations
To avoid worrying about pest control and disease management, take preventative measures. You should also devote time to proper bush care.

Timely preventive treatments
You can prevent the appearance of cabbage pests using the following methods:
- Carefully remove and dispose of plant debris after harvesting the cabbage heads. Burning them is recommended;
- Dig up and level the garden soil in the fall;
- Protect your garden beds with covering material. This is the simplest method for preventing pest attacks;
- In the spring and summer, weed. Harmful insects nest in weeds and then migrate into the garden beds. Weed rape and field pennycress especially carefully.
Proper care of the plant
To prevent pests and diseases, follow these rules:
- timely mowing of weeds;
- removal of all debris from the garden beds;
- Planting bushes at an optimal distance from each other will ensure ventilation and prevent dampness;
- compliance with crop rotation.
There are many ways to get rid of pests and diseases. The main thing is timeliness. Only a prompt (or better yet, early) response will allow you to get a rich harvest from your cabbage beds.











