- The benefits of propagating plums yourself
- Methods and technology for growing a plum orchard
- Cuttings
- When to prepare cuttings
- How to store properly
- Rooting and planting in the ground
- Root shoots
- How to take a sprout
- Technology of carrying out works
- The method of propagation by layering
- Air
- Ground
- Seed method
- Harvesting seeds
- Stratification and planting of seeds
- Transplantation to an open area
- Will the plum tree bear fruit?
- Is it necessary to instill culture?
- Mistakes of novice gardeners
There are two ways to increase the number of fruit trees on your property: buy your favorite seedlings or propagate the plants yourself. Plums tolerate transplanting well., and the propagation technology has long been known and is described in many gardening textbooks. On the internet, you can find many useful tips from experienced gardeners on rooting plum tree cuttings and descriptions of the root sucker propagation method.
The benefits of propagating plums yourself
By increasing the number of plum tree plantings, you can save significantly on the purchase of planting material and grow healthy seedlings adapted to growing conditions.
The main advantages of propagating plums yourself include:
- Guarantee of variety and health of seedling.
- Hardening and acclimatization of the plant to the upcoming growing conditions.
- Saving money on the purchase of planting material.
Moreover, growing a fruit orchard yourself is a fun and engaging activity. Gardeners gain new experience in plant care.
Methods and technology for growing a plum orchard
Proven methods of propagating plums include:
- seed method;
- cuttings;
- propagation by layering;
- root shoots.
All of these methods can be used to increase the fruit tree population on your own property or in commercial plum cultivation. When growing plum seedlings from seeds, grafting the future trees is essential; otherwise, the resulting plum will be a wild variety that has lost its varietal characteristics.

Cuttings
This method is one of the simplest; even a novice gardener can handle it. Typically, green plant branches are chosen for cuttings; they root better and establish themselves more quickly in their new location.
When to prepare cuttings
The optimal time to prune plum cuttings for propagation is in summer, at the end of July. Cuttings are made in the morning or evening. A green shoot, 30-40 centimeters long, is cut from the tree. This is divided into several pieces, approximately 10-15 centimeters long. Approximately 4-5 leaves should remain on the cutting.
Cuttings can be stored until next year. Before planting, place the cuttings in water containing Kornevin or a growth stimulant for 24 hours. During this time, prepare the bed or flower pots: disinfect the soil, loosen it, and apply fertilizer.

How to store properly
The cut branches do not have to be planted in the ground immediately; they can be stored in the refrigerator at a temperature of +2…+4 until the next season. C. For storage, use thick cuttings; thin specimens will quickly dry out and die.
Cuttings can be stored in a basement, but the room must be dry and dark. Before planting, trim the lower end of the branch with sharp scissors or pruning shears.
Rooting and planting in the ground
Plant the cuttings vertically in prepared soil, spacing them 10 centimeters apart, and plant the cuttings 5 centimeters deep. It is recommended to cover the beds or individual containers with plastic film; jars can be used for pots.

To quickly root the branches, the optimal temperature in the beds should be +25 The root system formation process will take about a month. It is recommended to water the plants every third day. The plants need to be ventilated. The first application of fertilizer is done when leaves appear on the branches, approximately a month later, immediately after the plastic coverings are removed.
Root shoots
This is a common method for propagating plum trees, and a very successful one at that. It's important to remember that the best cuttings for propagation are those located as far away from the mother tree as possible.
How to take a sprout
In the fall, the mother root between the mature plant and the sucker must be severed. The seedling is carefully dug up and immediately transplanted to its permanent location. Further cultivation of the young plant follows the variety's recommendations.
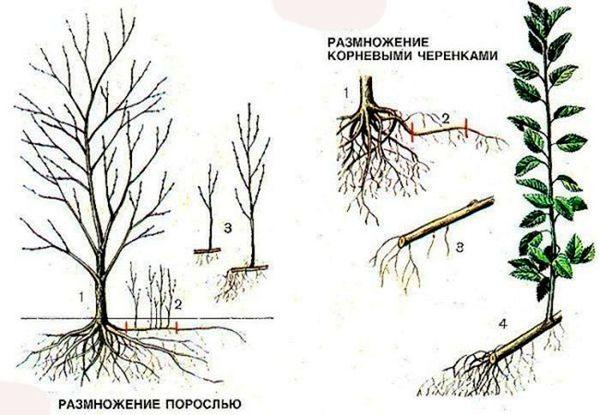
Technology of carrying out works
The main stages of the work:
- Cut down the remote sapling from the main tree.
- Cut off the mother root.
- Transplant the plant to a permanent location.
The severed root should be sprinkled with ash and the cut sealed with clay or garden pitch. The area around the trunk is loosened and mulched with humus. A hole is prepared for the young seedling and fertilized. The root is carefully straightened, covered with soil, compacted, and watered.
The method of propagation by layering
Spring method for propagating plums. The soil should be warm, with an optimal temperature of at least +12°C. C. There are two methods of propagation by layering: aerial and terrestrial.
Air
The procedure is performed in April-May, approximately a week before flowering. During this period, the plant actively absorbs sap, the wood becomes elastic, and metabolism accelerates. The tools needed for creating the aerial shoot include:
- pruning shears or a sharp knife;
- root growth stimulator;
- dark, dense film;
- moss or coconut fiber;
- duct tape and a syringe.
Preference is given to 2-3-year-old branches; green shoots from the previous year are also ideal. At the base of the stem, make two 1-centimeter-deep cuts with a knife. The bark between the cuts is carefully scraped away, creating a so-called ring cut. Two more cuts are made just above the ring cut, 2 centimeters away.

Small wood chips or matches are inserted into these grooves. The circumferential cut is treated with a growth stimulant. Using electrical tape and film, moss (preferably sphagnum) or coconut fiber is secured to the "damaged" part of the branch.
During the summer, the ring-shaped cut should be watered. To do this, make small holes in the film and water with a syringe. In late fall, the seedling is detached from the mother plant, transplanted into the ground, and insulated for the winter. This procedure is carried out approximately a month before the onset of frost.
Ground
Plum trees with low branches are suitable for this method. The selected branch is bent to the ground and a small cut is made where it meets the ground. Several matches are inserted into this cut.
To ensure the branch is securely attached, it is secured with wire and topped with nutrient-rich soil. Approximately 20 centimeters of the top of the bent stem should remain above ground. The rooted shoot is separated from the main tree in late fall or early spring.
Seed method
Plums are grown from seed pits indoors to create rootstocks for cuttings or layering. This method is not suitable for producing full-fledged fruit trees. Propagating the variety and increasing the number of trees by seed alone is not possible.

Harvesting seeds
Seeds are collected in the fall. Seeds are taken from ripe fruits and completely removed from the pulp. The seeds must be thoroughly dried and prepared for storage and stratification.
Stratification and planting of seeds
Stratification is the preparatory treatment of seeds for sowing. It lasts six months. The seeds are soaked in water for 24 hours, then dried and placed in a mixture of sand and sawdust, then refrigerated. After some time, the seeds are ready for sowing.
Planting of seeds is carried out in autumn or early spring, as soon as the soil thaws.
Transplantation to an open area
Young seedlings can be planted in beds in the spring when they have 4-5 true leaves. Space plants 20-30 centimeters apart. About a year later, graft cuttings from cultivated plums onto the young plants, thereby assigning a specific variety to them. Care for the shoots is the same as for mature trees.
Will the plum tree bear fruit?
Plum trees grown from layers or cuttings begin to bear fruit in the third or fourth year after planting in their permanent location. Trees grown from seeds will only produce fruit if grafted from a cultivated variety. Without grafting, there is a high risk of producing wild trees.

Is it necessary to instill culture?
Grafting a plum tree is a conditionally mandatory recommendation. Without it, the tree will grow and even produce fruit. Grafting is recommended for the following reasons:
- To enhance the varietal advantages of the plant.
- Replace one plum variety with another.
- Grafting onto frost-resistant rootstocks significantly improves the trees' resistance to cold and frost.
- Reduce the height of a tree by grafting onto a dwarf rootstock.
Varietal grafted plums are more resilient plants, are immune to various types of fungal diseases, and have better frost resistance.
Mistakes of novice gardeners
Although plum propagation seems simple, novice gardeners can make a number of mistakes. When growing plum seedlings, it's important to:
- Observe the planting dates for young seedlings.
- For propagation, cuttings and layers must be taken from healthy trees.
- When growing plums from seeds, it is necessary to stratify the seeds.
- Choose the right location and soil for your future fruit garden.
- Do not cover the seedling with soil above the grafting level.
- At the initial stage of plant growth, it is necessary to maintain humidity in the trunk circle and water it regularly.
- When storing cuttings, it is important to maintain the correct temperature conditions.
- Avoid dense plantings.
- Do not grow plum trees in acidic soil.
Plum trees grown from small branches and then grown into beautiful fruit trees producing a bountiful harvest of fragrant fruit are the ultimate reward for gardeners. By following proper plant cultivation and care, you're sure to reap a rewarding harvest and increase the variety of your orchard's fruit without unnecessary investment.











