- Garden hibiscus plant and its varieties
- Syrian hibiscus (Hibiscus syriacus)
- Ternary
- Hybrid
- Terry
- Tree-like
- Bushy
- Grassy
- Features of flowering of garden crops
- Landing
- Deadlines
- Selecting and preparing a site
- Direct landing
- Outdoor care
- Watering
- Fertilizer
- Trimming
- Transfer
- Pest control
- Preparing for the winter period
- How does a plant reproduce?
- Seeds
- Cuttings
- By dividing the bush
- Air layering
- Dividing rhizomes
Plants from the tropics and subtropics are widely used to decorate gardens in temperate latitudes. Breeders offer new species and varieties of vibrant ornamental plants adapted to harsher growing conditions. Propagation and care of garden hibiscus are largely the same as those for breeding and growing other flowers.
Garden hibiscus plant and its varieties
The natural habitat of hibiscus is the subtropical and tropical zones. Cultivated species are grown in continental climates in open areas and greenhouses.
The main botanical characteristics of the genus:
- Flower. Large, up to 8-40 centimeters, corolla (single or double). Bright color, with shades of white, red, and purple.
- Leaves. Size: up to 5-15 centimeters. Bright green. Toothed, on petioles.
- Seeds. Seed capsule.
- The root system is superficial.
The above-ground part can grow in the form of:
- herbaceous stem;
- tree-like stem;
- subshrub/shrub.
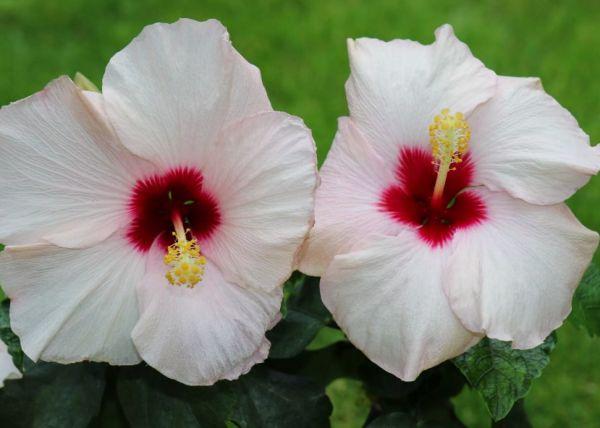

Herbaceous and tree-like hibiscus grow to 80-150 centimeters. They are used in landscaping to create zoning within a garden plot.
Shrub species reach 3-4 meters and are grown as individual stems for landscaping or as hedges.
Syrian hibiscus (Hibiscus syriacus)
An ornamental plant; depending on growing conditions and crown formation, it can grow as a bush or a small tree. The bushy variety grows up to 1 meter, while the standard variety reaches up to 5 meters. The flowers are double or single, up to 10 centimeters in size. The corolla is white, various shades of red, or white and red. The first flowering occurs 3-4 years after planting, and the blooming period lasts for 2 months.

Ternary
A distinctive feature of this species is that the buds open at sunrise and close when the sun reaches its zenith. The bush grows up to 90 centimeters tall. The flowers are small and two-toned: lemon-colored petals and a bright red center. The flowering period is 30 days.
Hybrid
Hibiscus, a cross between American species, grows as a straight-stemmed tree up to 3 meters tall. The leaves fall in winter. The buds tend to change color from white to pink.
Terry
The China rose is a double-flowered variety. In the central part of the country, the evergreen hibiscus is grown in greenhouses and hothouses. This ornamental plant blooms throughout the summer and fall.
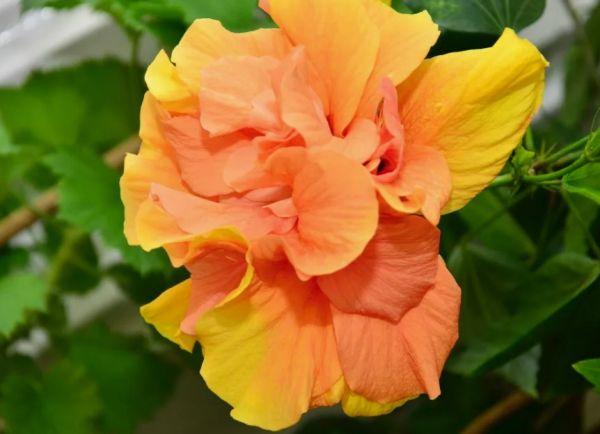

Tree-like
Hibiscus grows up to 3 meters in height and is resistant to temperature fluctuations and frost. The color palette varies depending on the variety. Blooms profusely from early summer until late September.
Bushy
In early October, the shrub sheds its leaves. Hibiscus grows little annually. Six to ten stems emerge from the rhizome. The maximum height does not exceed 1.5 meters. Budding occurs in summer and early fall. The flower size is 25 centimeters.
Grassy
Herbaceous hibiscus May have one or several growth and flowering cycles. In annual plants, the above-ground portion dries up each fall. The following spring, new shoots emerge from the roots and basal stems. Perennials retain dense, thick stems without leaves over the winter for up to 5 years.

The shoots reach a height of 1 meter. The flower shape is simple in annuals, while double in perennials. The corolla diameter can reach 40 centimeters. The flowering period depends on the climate zone: in southern regions, hibiscus blooms from late May to late September; in northern regions, from mid-July to early September.
Features of flowering of garden crops
Hibiscus blooms throughout the warm season: from late May to mid-September. A characteristic feature of hibiscus is the short blooming of its buds (10-12 hours) and their replacement by new ones within 14-12 hours.
Herbaceous hibiscus have larger flowers than tree-like varieties. Double-flowered varieties are planted outdoors in the southern regions, while single-flowered varieties are planted in the northern regions.
The time of flowering depends on the method of propagation: by seeds - 3-4 years after sowing, by cuttings - after 2 years, by dividing the root - the following year.
Landing
Growing hibiscus doesn't require any special agricultural practices, as the plant is easy to care for and tolerates both low and high temperatures. However, soil and lighting requirements must be met when planting.
Deadlines
The best time for planting is late May or early June, on a warm, windless day. During this time, recurrent frosts are rare, and hot, dry weather hasn't set in. These climatic conditions are essential for the plants to establish and germinate.
Selecting and preparing a site
All hibiscus varieties require good light, but avoid harsh ultraviolet radiation. The plant will thrive in diffused sunlight. Tree-like varieties thrive in cross-ventilation, which is unfavorable for herbaceous hibiscus.
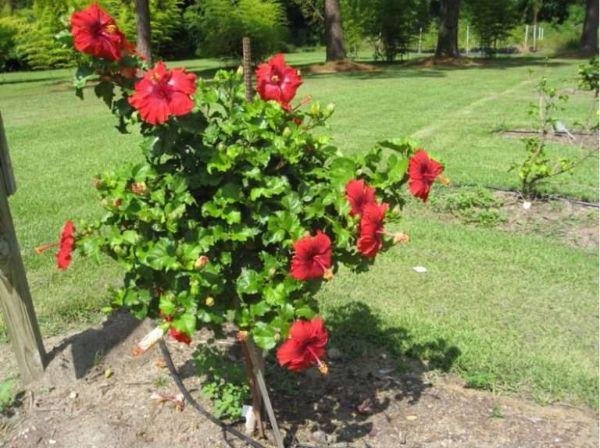

One flower in the garden requires an area of 1.5 to 3 square meters, depending on the variety. The soil should be neutral, structured, with a high humus content.
Direct landing
To plant properly, you need to prepare a hole of sufficient size. It should be deeper and wider than the root ball of the seedling. A mound of sand and humus mixture is placed at the bottom and watered with warm water.
The seedling is removed from the container by transshipment, after thoroughly moistening the soil. The root ball is placed over a moist sandy soil substrate, carefully spreading the roots. The soil is lightly compacted, the seedling is generously watered with sun-warmed water, and protected from direct sunlight for 3-5 days.

In regions with cold winters, the seedling is planted slightly deeper into the soil to protect it from freezing. In warmer climates, hibiscus is planted no deeper than 20-40 centimeters, based on the volume of the root system.
Outdoor care
Caring for hibiscus during the growing season is not particularly difficult.
Watering
How often and how much watering is needed depends on the weather and the plant's age. Young hibiscus plants are less drought-tolerant than mature ones. Until the plant reaches a height of 10 centimeters, ensure the soil does not dry out completely.
Misting is helpful to increase air humidity. This tropical plant may drop leaves and buds if air humidity drops below 60%. Water and humidify in the evening, before sunset.
Fertilizer
Hibiscus responds well to organic fertilizers and ash. At the beginning of the growing season, the plant is fed with mullein diluted in water at a ratio of 1:10. From June to August, the flowers are given foliar feeding. In September, ash is applied to the bush at a rate of 200 grams per square meter.

Trimming
Do hibiscus need pruning? Tree and shrub varieties require crown shaping and flowering stimulation.
During the growing season, 4 prunings can be carried out:
- Before leaves and buds appear, the branch is cut back by 1/3 to encourage buds to appear on the side shoots.
- During the summer, dried, weak, insect-damaged, and disease-damaged branches are removed. Pruning is done down to healthy wood.
- During the summer, on a bush with abundant branching, cut back shoots extending beyond the crown by a third, and remove branches growing toward the trunk.
- In autumn, in early September, after flowering has finished. Pruning includes the same procedures as for the previous three types.
The branch is cut at an angle: the top edge should be wider than the bottom. Branches are shortened by no more than two-thirds of their length. Complete branch removal is performed if the plant is infected, to allow it to recover.

Transfer
Hibiscus can grow in the same location for many years. Mature, established plants should be repotted no more than once every three years. Young plants can be repotted annually. Preparing and relocating hibiscus plants is similar to planting seedlings.
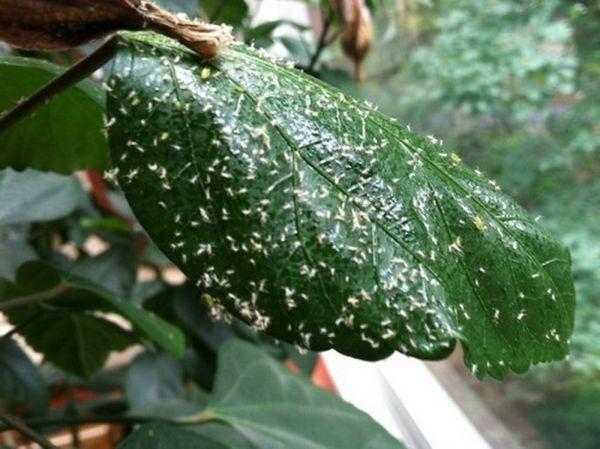
Pest control
Hibiscus leaves and buds are attractive to many pests:
- aphids;
- fungus gnats;
- thrips;
- Gauls;
- mealybug;
- spider mite.
All insects, with the exception of fungus gnats, which can be effectively controlled with a soap solution, are destroyed by treatment with insecticidal preparations.

Preparing for the winter period
To ensure successful wintering, with the onset of September the plants are cut and added to the soil potash fertilizers and water generously. After 2-3 days, mulch the soil around the bush. For the winter, when temperatures drop to +5°C (41°F), cover the hibiscus: bend the branches to the ground and cover them with windproof and waterproof fabric. Arches are installed over low-growing bushes, creating a greenhouse-like shelter.
How does a plant reproduce?
To propagate hibiscus, seeds, cuttings, dividing the bush, and grafting are used.
Seeds
Seeds collected in the fall must undergo stratification. To do this, they are placed in a cool place for 30 days. In March, the seeds are placed on a damp towel, wrapped in plastic to prevent the fabric from drying out, and left for a week.
After 7 days, the swollen seeds are sown in a prepared container with loose soil (a mixture of sand, peat, leaf mold, or a ready-made potting mix for indoor hibiscus). The seeds are laid out in even rows on the surface, spaced 5 centimeters apart, sprinkled with a mixture of river sand and peat, and watered with a spray bottle.

Cover the container with glass and place it in a warm, well-lit area. Sprouts emerge in 21-25 days. After the third and fourth leaves appear, the plants are transplanted into cups. The seedlings are ready for planting when they have 6-8 leaves. When grown from seed, the characteristics of hybrid varieties are not preserved.
Cuttings
To propagate hibiscus, in early summer, cut the top of a young, healthy shoot 10-15 centimeters long at an angle. Leave the top leaves on the cutting, and place the cutting in a growth stimulator for 6 hours. Fill a pot with at least 1 liter of potting soil and water with warm water. Make a 5-centimeter depression in the soil and place the shoot in it. Firm the soil and water again.
The pot is placed under a plastic cover to protect it from sun and drafts. Rooting takes about 2-3 weeks, after which the seedling is transplanted to its permanent location.
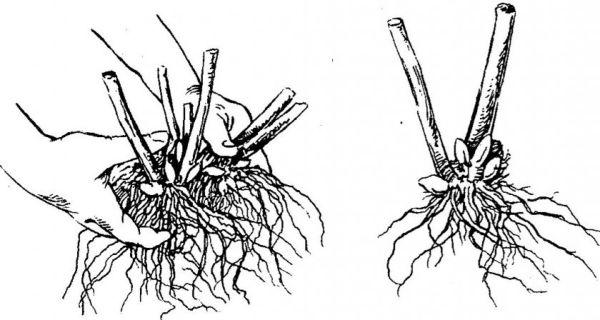
By dividing the bush
Perennial bushes are suitable for dividing. In the spring, the bush is removed from the ground. The rhizome is carefully cleaned of soil and divided into 2-3 parts with a sharp knife. 15 centimeters of the stem and the apical leaves are left on each part of the root, and the rest is trimmed off. The rest of the procedure is the same as planting a seedling.
Air layering
Hybrid varieties are more demanding than species varieties. Grafting a scion onto a rootstock produces flowering within the same season. A 2-3-year-old hibiscus is selected as the rootstock in early spring. The scion should have 3-4 buds. The branch is cut into a wedge 3 centimeters long. The shoots are of equal thickness.
The top of the rootstock is removed, leaving a 30-centimeter (12 in) stem. Using a budding knife, make a 3-centimeter (1.2 in) cut in the center of the trunk. The scion is inserted into the cleft, aligning the cambium layers, and firmly attached to the rootstock.
The grafting site is covered with a plastic bag with holes for ventilation. Swelling of the buds on the rootstock means that it is time to remove the protective film.
Dividing rhizomes
Herbaceous hibiscus are propagated by root division. The above-ground portion of annual species dies back in the fall; for perennials, it is cut back to 5-7 centimeters in late fall. In the spring, before stem growth resumes, the rhizome is dug up and divided and replanted using the same method as for tree/shrub hibiscus.











