- Description and Features
- History of origin
- Properties
- Caloric content
- Benefits and harms
- Acidity
- Bush characteristics
- Vine
- Bunch
- Productivity
- Taste qualities
- Winter hardiness and drought resistance
- Disease resistance
- Applications of berries
- How to plant correctly
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Site selection and preparation
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering
- Top dressing
- Mulching
- Garter
- Disease prevention
- Oidium
- Powdery mildew
- Anthracnose
- Chlorosis
- Rubella
- Bacteriosis
- Bacterial cancer
- Protection from birds and pests
- Preparing for winter
- Pruning and shaping
- Methods of reproduction
- Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- Harvesting and storage
- Taste and quality of wines
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
Winemakers around the world have been familiar with the Merlot grape for hundreds of years. Today, it is considered one of the most sought-after varieties for wine production, cultivated in virtually all countries of Europe, the CIS, America, and Africa.
Description and Features
Black Merlot grapes are a technical variety of fruit crops, used to make wines and drinks, and can also be consumed fresh if desired.
History of origin
The Merlot grape variety originates in the French province of Bordeaux. The first mentions of this varietal date back to the 14th century, but that's where the history of the Merlot grape ends. Thanks to biologists, DNA analysis of the fruit was conducted in the late 1990s, which accurately determined the grape varieties used to create the Merlot variety, so popular among winemakers.
The originators turned out to be Cabernet Franc grapes and the Madeleine Noir des Charentes variety.
Note: Merlot means blackbird in French.
Properties
Industrial grapes always have unique characteristics and properties unique to that particular fruit variety. To understand how and why Merlot grapes are used, it's important to familiarize yourself with their basic characteristics.

Caloric content
The main components of grapes are various types of sugars and acids. The average calorie content of Merlot grapes per 100 grams of fresh grapes is 63-65 kcal.
Important! The more sunlight and heat grape clusters receive, the sweeter and more caloric they become.
Benefits and harms
Merlot grapes contain a huge amount of useful substances and various groups of vitamins.
Fresh dried fruits are used to prevent and treat cardiovascular diseases and colds, eliminate gastrointestinal disorders, stabilize the nervous system, boost immunity, and relieve insomnia and stress.
The leaves, seeds and fruits of the berry crop are used in the production of cosmetic products.
It is not recommended to consume black Merlot grapes if you have high blood sugar or individual intolerance to the product.

Acidity
The level of sugars and acids in grapes directly depends on the climatic and weather conditions of the growing region.
Average sugar levels are up to 22%, acid levels are up to 8%.
Bush characteristics
This fruit tree is characterized by rapid and vigorous growth of bushes with strong yet flexible branches. The leaves are large, with serrated edges, and their color varies depending on the stage of the growing season. In early spring, the leaves are bright green, later acquiring a beautiful bronze hue. In autumn, the leaves turn yellow and develop small red spots.
The cluster-shaped inflorescences bloom with small flowers, in the place of which fruit ovaries are formed.
Important! Merlot grapes are self-pollinating and do not require neighboring pollinators.
Vine
The fruiting shoots are spreading, slightly hairy, grayish in color, and splashed with pink. The vines ripen completely before the first frost.
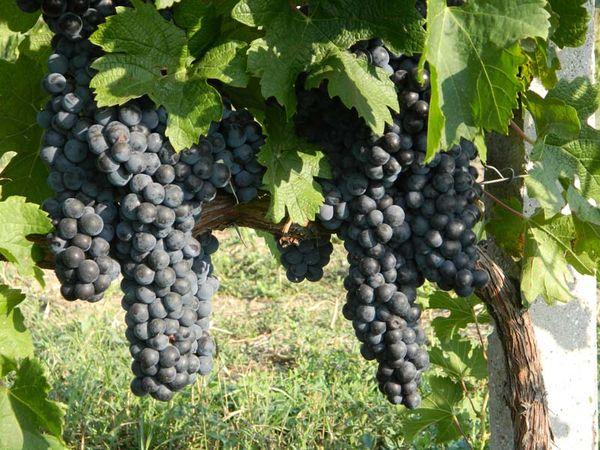

Bunch
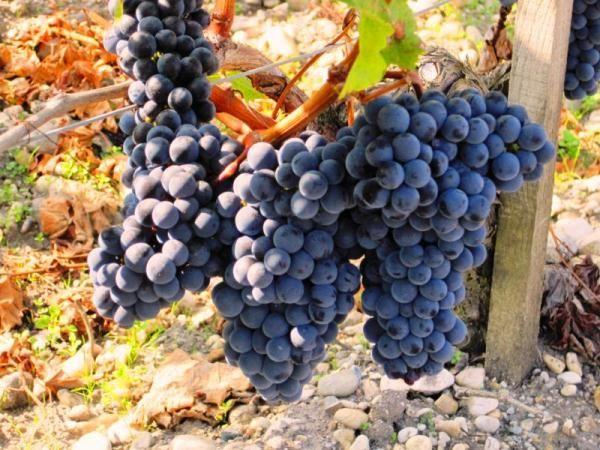
Merlot grapes have beautiful cone- or cylindrical-shaped clusters, up to 17 cm long, 10 to 12 cm wide, weighing up to 150 g, with dark blue berries.
The fruits are round, weighing up to 1.5 g, almost black in color when ripe, with a dense protective waxy coating.
Productivity
The berries ripen 153-164 days after the end of the flowering phase.
The yield of fruit crops depends on climatic conditions and proper care.
With favorable weather and timely agricultural technology, one grape bush can produce up to 15-17 kg of ripe berries.
In industrial quantities, up to 6 tons of produce are harvested from 1 hectare of land.
Taste qualities
It is important to remember that the Merlot grape variety is a technical crop and is intended for the production of wines and beverages.
The berries have a dense skin and very juicy, sweet and tart pulp with a specific taste and aroma.
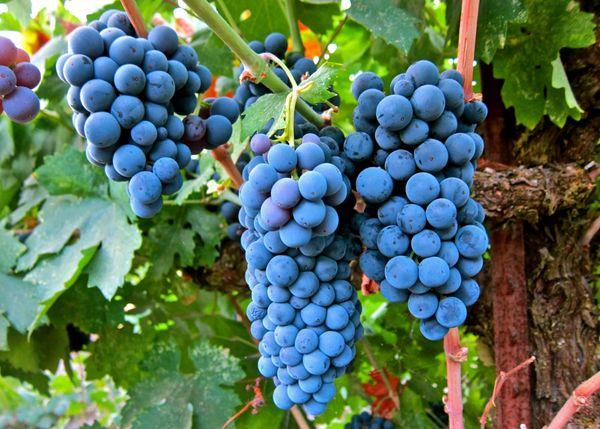

The fruits consist of 74% juice and only 22% peel.
Important! For many people, this grape variety's berries cause irritation to the oral mucosa due to the concentration of substances.
Winter hardiness and drought resistance
The fruit crop is frost-resistant and easily tolerates winter temperatures down to -29 degrees, but is susceptible to recurrent spring frosts and does not tolerate prolonged drought.
Disease resistance
Merlot grapes have excellent natural immunity to most fungal and viral diseases. Furthermore, the black berries, with their distinctive aroma and flavor, are rarely attacked by pests.
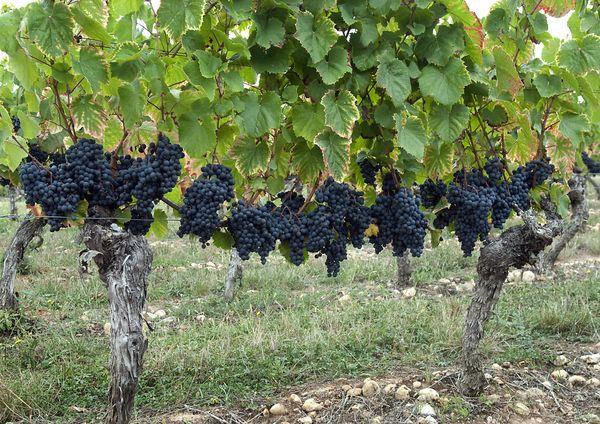
Applications of berries
The main purpose of ripe Merlot grapes is winemaking.
Depending on the conditions and timing of the berries' ripening, dry, table, or dessert wines are made from the fruit. The berries are also added to juices and nectars.

How to plant correctly
The future yield of berry crops depends on the quality of the planting material, the chosen location and the composition of the soil.
Recommendations for choosing deadlines
The timing of planting seedlings in open ground depends on the climatic and weather conditions of the growing region.
In southern regions, grapes are best planted in the fall. In temperate and cold climates, the fruit crop is planted outdoors in the spring.
Important! When planting Merlot grapes, it's important to consider the intended uses for the berries, as the wine's flavor depends on ripening time.
Site selection and preparation
Sunny sites on slopes and plains, sheltered from northerly winds and drafts, are selected for planting. A south-facing plot is ideal for growing Merlot grapes.
Fruit crops produce higher yields in dry mountain soils; clay soil mixed with river sand imparts a delicate flavor and aroma to the berries. Grapes grown in calcareous soils have rich flavor notes, while sandy soils impart a softer texture to the berries.

It is not recommended to grow fruit crops in lowlands, in areas with high groundwater levels, or on swampy soils.
The land plot is prepared 4-6 weeks before the planned planting work.
- The soil is dug deeply, cleared of debris and weeds, and thoroughly loosened.
- Humus, organic matter and mineral fertilizers are added to the soil.
- 12-14 days before planting, dig holes 60-80 cm deep and wide.
- The distance between plantings is from 1.2 to 1.5, between rows up to 3 m.
- A drainage layer and fertile soil are placed into the planting hole and watered from above.
Important! Merlot grapes require support for growth and development. Stake stakes, special structures, or trellises are used to support the fruit bushes.
How to select and prepare planting material
The further growth and fruiting of grape bushes depends on the quality of the planting material.
- Seedlings are purchased from trusted nurseries or special centers.
- Plants that are 1-2 years old take root and establish themselves best.
- A thorough inspection of the plant's appearance is carried out for damage and diseases.
- The trunk of the seedling is straight, uniform in color, with the obligatory presence of fruit buds or green leaves.
- The rhizomes are well developed and moist, without signs of rot or fungal infections.
Tip! Place the seedlings in a container of warm, settled water the day before planting them outdoors.

Planting diagram
Before planting, the roots of the seedlings are trimmed, leaving only the strongest and longest shoots.
- The plant is placed into the planting hole at a slight angle.
- The roots are evenly spread out in the hole and covered with fertile mixture.
- The soil under the bush is carefully compacted and watered.
- The plant is tied to a support.
After completing planting work, the tree trunk circle is mulched with peat or dry grass.
Care instructions
The health of berry bushes, the amount of harvest, and the taste of berries depend on proper and timely care.
Watering
Grapevines are watered depending on weather conditions. During drought, watering is increased; during rainy seasons, it is reduced.
Irrigation work is especially important during the period of flowering, formation of ovaries and ripening of the crop.
According to the standard schedule, irrigation work is carried out once a month, watering the bushes with settled water.
After watering, the soil is loosened and weeded.

Top dressing
For better growth, development and fruiting, grape bushes require additional feeding.
Berry crops are fertilized 4-5 times throughout the growing season. In early spring, nitrogen fertilizers and organic matter are added to the soil. During the active growing and fruiting period, grapes are fed with phosphorus and potassium. After harvest, the bushes are fertilized with organic matter and a mineral complex.
Mulching
Mulching the tree trunk circle allows you to avoid frequent loosening and weed removal, and also insulates the root system before winter frosts.
Organic materials are used as mulch.
Garter
As the grapevines ripen, they are subjected to a significant load, which the delicate fruiting shoots may not be able to withstand. Therefore, the grapes are tied to special structures or trellises.

Disease prevention
Although Merlot grapes have natural immunity to diseases and pests, improper plant care and poor weather conditions increase the risk of certain diseases.
Oidium
A fungal infection of the above-ground parts of the plant. Leaves, shoots, fruits, and ovaries become covered with a whitish, flour-like coating. The berries rot and spoil, accompanied by an unpleasant, musty odor.
For treatment and prevention, fruit bushes are sprayed with fungicides or sulfur-based preparations.
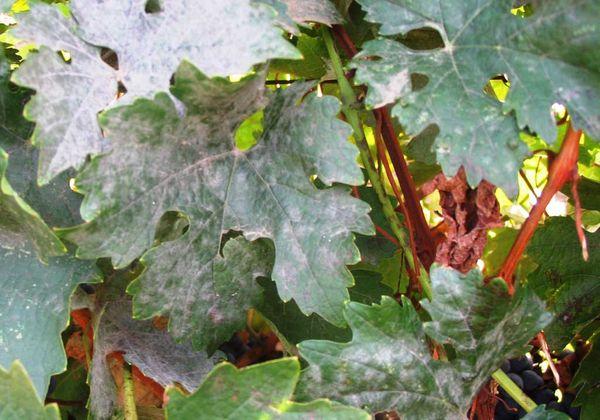
Powdery mildew
The disease, caused by a fungus, is manifested by the drying up and falling off of leaves, flowers and ovaries.
To prevent damage, in early spring, the bushes are sprayed with chemical or biological preparations.

Anthracnose
The disease manifests as dark spots on all parts of the plant. Pinkish ulcers develop on the berries. Without treatment and prevention, the bunches and fruit shoots turn black and die.
To control the disease, fungicides containing copper or biological preparations are used.
Chlorosis
Chlorosis is manifested by yellowing of leaf blades and subsequent wilting of shoots.
To restore the plant's health, fertilizing and spraying the bushes with preparations containing iron are used.
Rubella
A fungal infection of the above-ground part of the plant, manifested as reddening and wilting of the leaf blades.
For treatment and prevention, chemical and biological plant protection products are used.
Bacteriosis
The disease manifests itself as ulcers on the branches and spots on the fruits; the buds and ovaries turn black and fall off.
Bordeaux mixture and biological preparations are used for treatment and prevention.

Bacterial cancer
Bacterial infection manifests itself in the form of light-colored tumors and growths throughout the plant.
In the initial stages, copper- and iron-based treatments are used, and the affected areas are excised. If the disease progresses rapidly, the bush is dug up and destroyed, and the soil is treated with specialized chemicals.
Protection from birds and pests
To prevent and protect grape vines from insects, thoroughly weed and loosen the soil, and mulch the area around the trunk. In early spring, spray the plants with chemicals or special infusions.
Birds also pose a threat to grapes. Decoys, shiny objects, special materials, and nets are used to protect against birds, making it difficult to reach ripe grapes.
Preparing for winter
Before the onset of winter dormancy, berry bushes are watered, fertilized, pruned, and the trunk circle is insulated with a layer of humus and spruce branches.
In regions with moderate and cold winters, grapes are bent to the ground, secured and covered with special fiber, wooden boxes or slate.
Pruning and shaping
Merlot grapes require annual pruning of old, damaged, dried out, diseased and pest-infested branches and shoots.
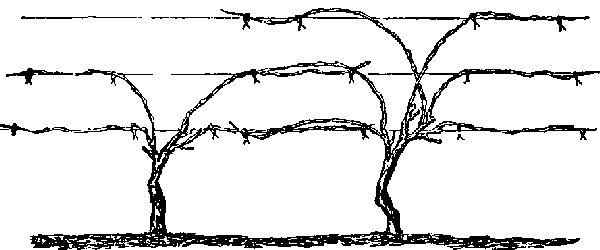
To shape the bush and increase yield, formative pruning is performed. For this, several strong branches and shoots are selected, and the rest are completely pruned.
Methods of reproduction
To increase the number of Merlot grapes in a garden plot, vegetative propagation methods using cuttings or seedlings are used.
For cuttings, select a strong, healthy shoot from a mature bush and prune it. The branch is divided into several cuttings with buds or leaves. The cuttings are treated with a growth stimulant and planted in a container with fertile soil. With the arrival of spring, the grown seedling is transferred to open ground.
Propagation by seedlings is the easiest and fastest way to get strong, healthy grape bushes.
- At the beginning of summer, the lower, strong shoot is selected from an adult plant.
- A small trench is dug in the ground, into which the layer is placed and secured.
- The shoot is covered with soil from above, leaving the upper part of the layer above the soil surface.
- During the growing season, the cuttings are watered and fed.
- In autumn, the rooted shoot is dug up and cut off from the mother bush along with the roots.
- The young bush is planted separately.
When propagating grapes by layering, the prepared seedlings quickly take root and establish themselves.

Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Having become familiar with the main characteristics of the fruit crop and the rules for growing Merlot grapes, you can draw conclusions about the advantages and disadvantages of the variety.
- Merlot grapes are easy to care for and grow.
- The variety is resistant to frost and temperature changes.
- Fast ripening of berries.
- High yield rates.
- Relative resistance to diseases and pests.
Note: Merlot is a commercial grape variety, but with proper care, its healthy berries are often eaten fresh.
Flaws:
- Fruit crops require special attention during the ripening period. Each wine variety requires a specific sugar content in the fruit.
- In rare cases, mold appears on the berries.
- When ripe, the berries fall off.
Otherwise, varietal grapes are completely undemanding, so they are accessible for cultivation even for novice farmers and gardeners.
Harvesting and storage
The harvest of ripe grapes is calculated based on future harvest plans. Each type of wine requires its own ripening period, acidity, and sugar content. Grapes overripen very quickly and lose the qualities needed for dry and table wines. In this case, winemakers produce dessert wines.
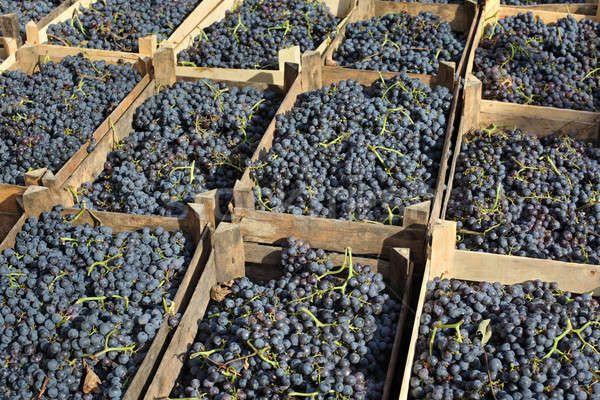

In special refrigeration chambers, Merlot grapes are able to maintain their marketable appearance for a long time, but the taste of the berries changes.
Taste and quality of wines
The taste and quality of wines made from fruit crops directly depend on weather conditions, the number of sunny days, soil composition, adherence to care rules, and the methods of growing grape bushes.
Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
The main recommendations from experienced gardeners and farmers boil down to proper and timely care for Merlot grapes. The quality and taste of wines depend on the ripening stage of the berries.











