- Necessity of the procedure
- Review of drugs
- "Topaz"
- Strobie
- Thiovit
- Ridomil Gold
- Bordeaux mixture
- Horus
- "Dnok"
- Quadris
- Vectra
- Falcon
- Folk remedies
- Soda solution
- Copper sulfate
- Colloidal sulfur
- Iodine solution
- The order and timing of spraying
- Peculiarities of disease control in rainy weather
- Anthracnose
- Gray rot
- White rot
- Mildew
- Preventive measures against pests
- Weeding
- Trimming
- Removal of infected parts
- Proper watering
- Mulching
- Top dressing
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
When growing grapes, the plants require careful attention and care. Warm, rainy weather encourages pests and diseases, which can reduce yields by a quarter. To preserve the fruit and their flavor, it's recommended to monitor climate conditions and adhere to a schedule of post-rain treatments, especially in July. Proper vineyard protection will prevent fungal infections and harmful insects.
Necessity of the procedure
After prolonged rainfall, grapes are very vulnerable. Splashes of water containing dirt can infect the stems with spores and bacteria found in the soil. Therefore, immediately after precipitation, the vines should be treated with special preparations, especially during the ripening period.
Review of drugs
No disease is a death sentence for a vineyard, and any ailment can be overcome. The right solution is a comprehensive approach, encompassing both disease prevention and timely treatment, which includes the use of the following effective products.
"Topaz"
A broad-spectrum fungicide helps protect grapes from anthracnose and mildew. Topaz can enhance the plant's defenses and suppress the spread of infection. It has a rapid action, beginning to kill fungi within a few hours of application.
 Important! When using, remember safety precautions, as Topaz is toxic to humans.
Important! When using, remember safety precautions, as Topaz is toxic to humans.
Strobie
The product prevents the outbreak of the disease, inhibits further spore development, and stops mycelial growth. "Strobi" is available as granules that dissolve instantly in water. Prepare the solution according to the instructions. Spray the leaves, vines, grapes, and the soil in the root zone. Apply the product twice over a period of 7-10 days. The final treatment should be carried out one month before harvest. It poses no danger to humans, birds, or animals.

Thiovit
This product is a fungicide and acaricide designed to treat fungal diseases and kill parasites. It comes in granules that dissolve easily in water. It has received high praise from gardeners because it disrupts the cellular structure of bacteria upon contact and inhibits their growth, without harming grapes and preserving their microflora.
Ridomil Gold
A systemic contact antimicrobial agent available in granule and powder form. It penetrates the plant, creating a barrier to fungal spore penetration throughout the entire crop—from roots to berries and tendrils.
Bordeaux mixture
This product is used to make Bordeaux mixture, which is used to combat anthracnose, mildew, rubella, and black rot. It acts quickly on infected areas, remains on the plant for a long time, and effectively protects grapes for up to a month.
Horus
A comprehensive product designed to combat grapevine diseases such as mildew, gray mold, moniliosis, and others. Its main advantage is its low toxicity. Available in waterproof granules, Horus destroys fungal spores and helps stop the parasite's life cycle.

"Dnok"
An insecticide, fungicide, and herbicide in one bottle. This potent product is used for industrial applications and is not recommended for small plots. Apply in early spring, before the sap begins to flow, at a rate of 8 liters per 0.1 hectare. This will protect the plant from powdery mildew, anthracnose, and leaf spot all season long.
Important! "Dnok" is a highly toxic drug and is extremely dangerous to humans. Therefore, it is important to take precautions and use it according to the instructions on the packaging.
Quadris
This fungicide has a long-lasting effect. It is used to protect and treat fungal diseases, as it kills fungal spores and stimulates and improves grape growth. Proper application ensures the therapeutic and preventative effect lasts for 2-3 weeks.

Vectra
A contact and systemic fungicide with protective action. Odorless. Available in 2 and 5 ml ampoules. Application during flowering is prohibited. Hazard Class 3. This product eliminates sporulation of phytopathogenic fungi, treats grapes, and limits damage.
Falcon
This product prevents the development of powdery mildew, rust, and powdery mildew on grapevines. Falcon provides long-lasting protection, is mildly toxic, and poses no environmental hazard. Pathogens are prevented from developing resistance to the fungicide's composition, allowing for use for several years.
Belongs to the 2nd class of danger for humans.
Folk remedies
Many gardeners successfully use folk remedies instead of chemicals to protect vineyards from fungal diseases and pests.
Soda solution
A versatile remedy that's useful for combating mildew, gray scurf, and other diseases. Spraying the above-ground parts of grapes with a soda solution during heavy rainfall can increase the sugar content of the fruit as they ripen and protect them from gray rot. To do this, prepare a mixture of 5 tablespoons of soda, 10 liters of water, and 20 ml of liquid soap.
![]()
Copper sulfate
This product is used to kill parasites and pathogens lurking under the plant's bark. For prevention, treat grapevines with a solution of 100 g of 1% copper sulfate diluted in 10 liters of water. For severe infestations, spray the bushes with 300 g of a 3% solution, previously diluted in 10 liters of water. This solution is recommended for use in cool and damp weather before bud break.
Colloidal sulfur
Colloidal sulfur is an inorganic fungicide in gray-yellow powder form, containing 80-95% sulfur and 5-20% additional substances. For preventative purposes, spray during bud break to prevent diseases on green shoots. Do not use during flowering. The treatment is effective at temperatures above 20°C (68°F); below this temperature, the product's effectiveness is reduced, as it kills pests and fungi in vapor. Do not spray at temperatures above 35°C (95°F), as this can cause burns on the leaves and fruit.

For prevention, use 40 g per 10 liters of water, and for treatment, use 100 g per the same volume of liquid. The protective effect lasts approximately two weeks, and the fastest effect occurs 3-4 hours after application.
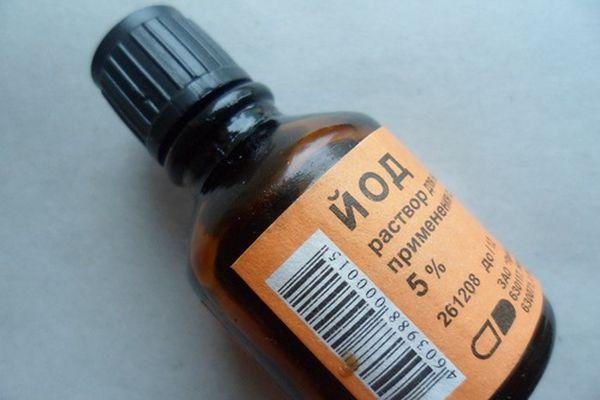
Iodine solution
An effective way to get rid of The treatment of grapes against gray rot is Treat bunches of grapes with 5% iodine when the fruit is gaining size and during ripening in rainy weather, diluting 0.5-1 ml per 1 liter of water. This solution not only protects the crop from diseases but also enriches the fruit.

The order and timing of spraying
Every gardener should develop their own schedule for preventative grape treatments. This schedule should be based on climate conditions, weather, grape ripening period, varietal characteristics, and the prevalence of diseases in the growing area.
Stages of spraying:
- In the spring, before flowering, spray the grapes with Bordeaux mixture and copper oxychloride to strengthen their immunity.
- After the first 3 rains at the beginning of flowering and fruit formation at temperatures above 10 degrees, use “Strobe”, “Quadris” or another complex product.
- After flowering, in the summer, when there is a lot of rainfall, systematically apply any of the fungicides until the end of July within 2 hours after the rain.
 Advice! When treating, pay attention to the parts of the grape plant that are most at risk of infection. Stems that come into contact with the soil during rainy periods should be thoroughly sprayed, as the fungicide's effect extends to the parts of the plant that are exposed to it.
Advice! When treating, pay attention to the parts of the grape plant that are most at risk of infection. Stems that come into contact with the soil during rainy periods should be thoroughly sprayed, as the fungicide's effect extends to the parts of the plant that are exposed to it.
Peculiarities of disease control in rainy weather
After rain in warm weather, the risk of vineyards becoming infected with fungal diseases such as anthracnose, gray rot, white rot, and mildew increases.
Anthracnose
This fungal disease affects all green parts of the grapevine, particularly young tissue. Its appearance is indicated by small brown spots with a dark white border, which subsequently enlarge and merge, then dry out and die. Shoots are also affected, becoming covered in necrotic, sunken, brown spots. Affected tissue cracks, forming deep ulcers. Stems become brittle, break, and dry out.
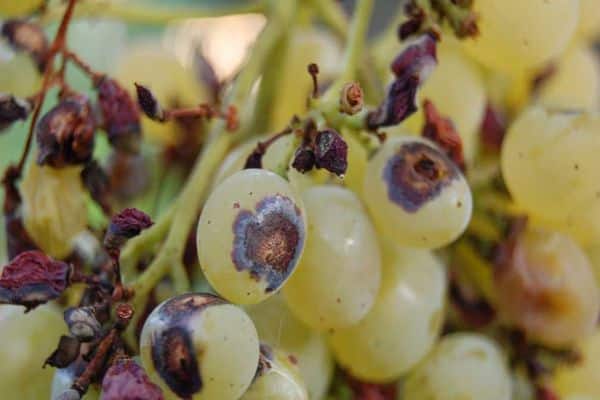

Treat the crop against anthracnose in spring and autumn with a 10% solution of ferrous sulfate, and after prolonged rains, use a 1-3% Bordeaux mixture.
Gray rot
The fungus prefers the green parts of grapes. Symptoms include brown spots on foliage covered with a film, necrosis of woody shoot tissue, drying of inflorescences and bunches, and brown, loose fruit skin.
To protect vineyards from gray mold, spray with "Dnok" before bud break. Use "Ortoftapan" during the growing season. After harvesting, fumigate the storage area with sulfur.
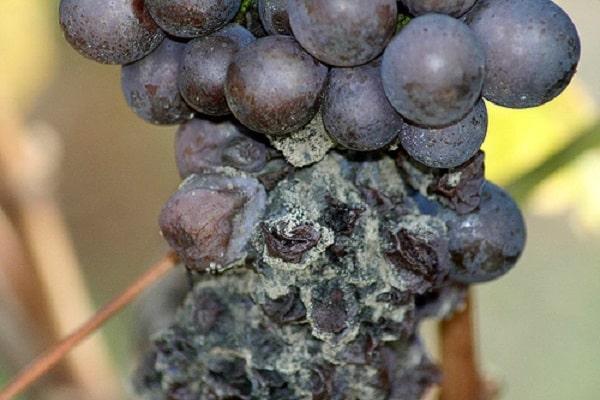

White rot
This fungal disease attacks green fruit in damp, warm weather. White rot can be diagnosed by the appearance of dirty-white bumps on the berries, followed by their shriveling and drying out.
A 3-4% Bordeaux mixture solution can be used to combat fungus. Spray the plant with it. Repeat the procedure after rainfall, when symptoms of infection appear.
Mildew
Downy mildew is considered one of the most dangerous grape diseases, affecting all parts of the plant. This downy mildew occurs after rainfall, so its development is primarily observed in conditions of frequent precipitation in the summer. In high humidity, the fungal spores travel in water droplets and penetrate the grape tissue.
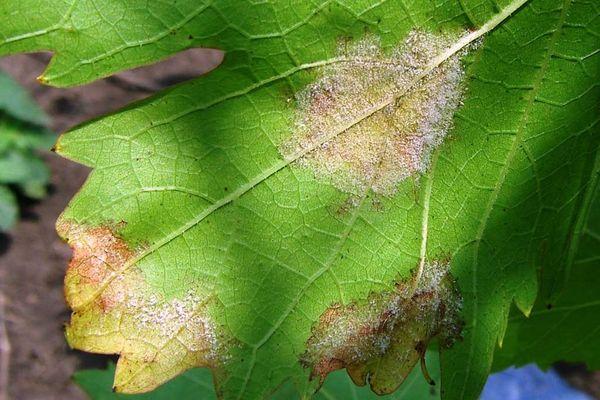

The disease is diagnosed by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of transparent spots up to 3 cm in diameter, colored yellow, on the outer surface of the leaves;
- the presence of a velvety white coating after precipitation in the form of rain, dew, fog;
- inhibition of growth and development of grape bushes;
- leaf fall;
- darkening of fruits - they acquire a blue and brown color and wrinkle.
To prevent mildew, spray with a 1% Bordeaux mixture after rainfall, before the spores penetrate the plant tissue. Suspensions such as copper oxychloride (0.5-0.8%) and Zineb (0.5-0.7%) can also be used for protection.

Preventive measures against pests
Preventative measures include operations and techniques that will not only increase the yield, improve the quality of berries, accelerate the ripening of fruits, and enhance their appearance, but also protect against dangerous pests.
Weeding
Timely weeding will help reduce the moisture level in the lower part of the grapes and prevent the development of diseases.
Trimming
Properly performed pruning will create favorable conditions for good aeration and sufficient lighting of all parts of the plant.
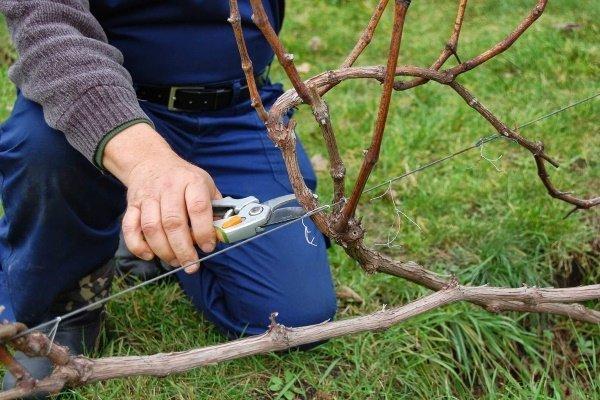

Removal of infected parts
When cultivating grapes, it is necessary to constantly inspect the plant and promptly remove all parts affected by pests and then burn them away from the site.
Proper watering
It is important to organize irrigation correctly, optimally moistening the soil and maintaining it in the condition necessary for the good development of grapes.
Advice! Water carefully at the roots, avoiding moisture getting on the plant's leaves.

Mulching
Mulching the soil around grape vines is essential. Humus or shredded coniferous trees can serve as mulch. This will prevent digging and disturbing the topsoil, which harbors fungal spores.
Top dressing
Adding nutrients will strengthen the grapes' immunity and increase their resistance to various fungal diseases.

Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
Growing grapes requires a thorough understanding of the science, and in the early stages of learning, a novice viticulturist must answer many questions regarding the prevention and control of diseases and pests during the rainy season. The advice and recommendations of experienced gardeners will help them with this:
- Treat grape plantings in the evening hours, after sunset.
- Spray from top to bottom for better absorption of the product.
- Use a sprayer equipped with a sealed pump.
- Use Bordeaux mixture on a windless day.
- Apply sulfuric substances when temperatures are below 30 degrees to avoid burning plants.
- When working with drugs, strictly observe safety precautions.
These recommendations will help you quickly overcome diseases and get a rich grape harvest.











