- History of the variety
- Description of the Mackintosh apple tree
- Dimensions of a mature tree
- Tasting evaluation of apples, scope of application
- Shelf life and transportability
- Characteristics of the culture
- Habitat
- Immunity to diseases and insects
- Resistance to sub-zero temperatures
- Pollination and self-fertility
- Ripening and harvesting times
- Productivity and annual growth
- Planting and care
- Dates and seating arrangements
- Preparing the site and planting hole
- Technology of planting seedlings
- Fertilizer and watering
- Preventive treatment
- Pruning and crown shaping
- Preparing the tree for winter
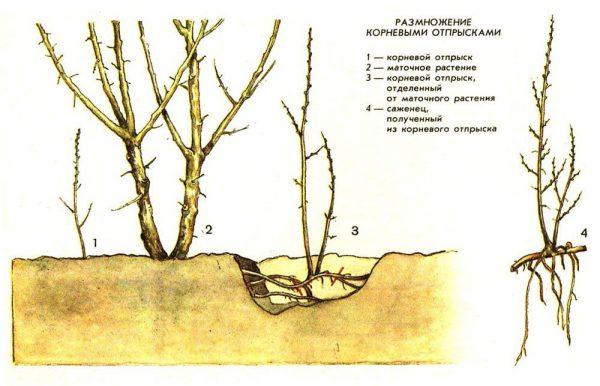
- How to propagate a tree
- Related varieties
- Daughter Mackintosh
- Black
- Cortland
- American Macintosh
Apples are the most popular fruit in the world. A huge number of hybrid varieties and subtypes of this tasty and healthy fruit have been developed. This easy-to-grow fruit is grown in both southern regions and cold northern climates. Over 200 years ago, the Mackintosh apple variety was developed, subsequently becoming the ancestor of many varieties and subtypes.
History of the variety
The variety's origins date back to the 18th century. Canadian farmer John McIntosh purchased a plot of land for his farm, where he discovered several apple seedlings. He replanted the trees, but by the mid-19th century, only one tree survived, which only ceased bearing fruit in the early 20th century.
It is this surviving apple tree that is considered the ancestor of the McIntosh apple variety.
In the last century, the McIntosh variety began to be actively cultivated in Canada and North America. Subsequently, the new fruit crop crossed the ocean and began to be grown throughout the European part of our continent.
Interesting! It was the Macintosh apple that became the main symbol and emblem of the company founded by Steve Jobs, known as Apple.
Description of the Mackintosh apple tree
In Russia and the CIS countries, the McIntosh apple variety is known as Autumn Red-Boked or Autumn Khoroshevka.
With proper and timely care, Mackintosh apple trees produce high yields, easily tolerate light frosts, and have a long shelf life when ripened, containing many vitamins essential for human health.
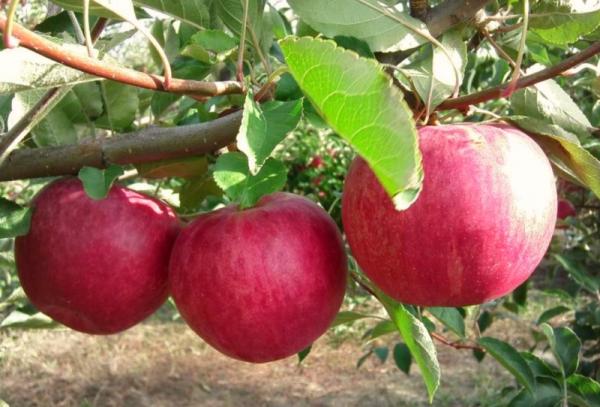

Dimensions of a mature tree
Fruit trees of this variety grow up to 5-7 m. The crown is elongated, pyramidal in shape with spreading, straight branches of a reddish hue.
The leaves are medium-sized, oval, and bright green. As autumn approaches, a yellowish bloom appears on the leaves, indicating the fruit is about to ripen.
The flowering period begins in mid- to late May and lasts 7-10 days. Apple trees begin blooming in the second year of growth. The first abundant harvests are produced in the fifth to seventh year of the tree's life.
Tasting evaluation of apples, scope of application
Experts rate the fruit's taste as exceptional. This is true, as the bright and beautiful fruits are not only delicious but also healthy. In Western countries, the McIntosh apple variety is a mandatory part of the diet in preschools and educational institutions.
The fruits are large, from 150 to 200 g, with juicy, sweet white flesh and a pronounced apple aroma.
The skin is thin, but protects the flesh well from damage. The ripe fruits are yellow or green, with a bright red or burgundy blush.
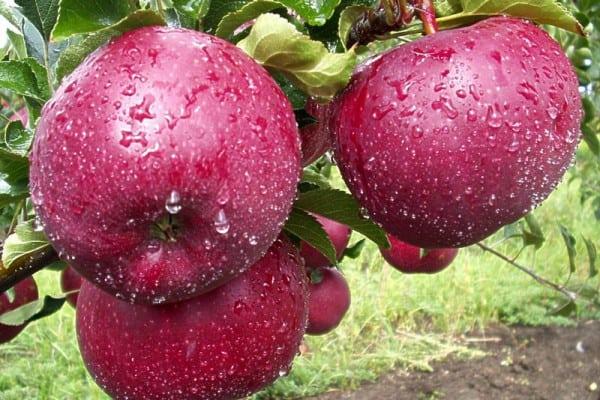

Ripe fruits are primarily intended for raw consumption.
McIntosh apples are used commercially to make baby food, juices, nectars, jams, and preserves. They are also dried, boiled, baked, added to desserts, and canned.
Shelf life and transportability
After harvest, apples ripen in storage for 2-3 weeks. Under proper storage conditions, autumn fruits retain their flavor and appearance for 3-5 months. The apples' thin yet strong skin allows them to be transported long distances without risk of damage.
Characteristics of the culture
Like any fruit crop, the variety has its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Apple trees bear fruit reliably every year.
- The fruit crop is unpretentious in care.
- Highly rated for its taste.
- Duration of storage of ripe fruits.
- Resistant to temperature changes and light frosts.
- The fruits contain a high content of vitamins and minerals.

The advantages of this variety include the fact that pruning of trees is not difficult.
Flaws:
- Unfortunately, the older the tree gets, the less fruit it bears.
- Fruit ripening occurs at different times.
- Fruit crops are susceptible to certain diseases and pests.
Important! Timely preventative tree treatments will significantly reduce the risk of pests and diseases.
Habitat
The Mackintosh apple tree is cultivated commercially in Canada, North America, Europe, and the CIS. In Russia, regions with southern and warm temperate climates are considered favorable for growing this apple variety. The largest plantings of this fruit tree are found in the Caucasus and the chernozem soils of the Lower Volga.

Immunity to diseases and insects
The main threat to trees is fungal diseases, to which apple trees are virtually vulnerable. If care guidelines are not followed, the risk of scab and powdery mildew spreading increases. Failure to prevent diseases at an early stage increases the risk of losing the fruit tree.
Also, don't forget about pests. Aphids pose a threat to the tree's green cover, and codling moths can destroy the entire harvest.
Resistance to sub-zero temperatures
In regions with moderate and warm climates, McIntosh apple trees easily survive winters. Small temperature fluctuations and short frosts do not affect the growth, development, or fruiting of the plant. However, prolonged frosts below -20°C (-4°F) cause the trees to freeze, which negatively impacts the following season's harvest.

Pollination and self-fertility
The McIntosh apple tree's fruiting doesn't depend on pollinating neighbors; even without them, the tree produces large fruit crops. However, neighboring fruit trees have a positive effect on the speed and quantity of fruit set and improve the flavor of ripened fruit.
Important! To ensure proper growth and development, apple trees are prevented from bearing fruit during the first 3-4 years of growth by removing flowers and ovaries.
Ripening and harvesting times
The trees ripen their fruits one after another. Harvesting of ripe fruit begins in late August and ends in October.

Productivity and annual growth
Gardeners and farmers have long appreciated the fruit crop's productivity. The apple tree bears fruit annually, yielding up to 200 kg of ripe, delicious fruit per tree.
The annual growth of the tree is from 7 to 9 cm during the growing season.
Planting and care
Timely planting of seedlings in open ground and proper care are the main factors influencing the lifespan of a fruit crop and its yield.
Dates and seating arrangements
Trees are planted in open ground in early spring or fall. Spring work is carried out before the first buds open. In the fall, fruit trees are planted depending on the region's climate. The key is to give the seedling 40-50 days to establish roots before the first hard frost.

When planting seedlings, consider the size of mature trees. Leave at least 1.5-2 meters between young plants, and 2 meters between rows.
Preparing the site and planting hole
To grow fruit trees, choose a well-lit site at a slight elevation. Close groundwater will cause rhizome rot and the spread of fungal diseases. Trees also do not tolerate strong cold winds and drafts.
The soil for planting is prepared in advance. If the seedlings are to be planted in the spring, the area is thoroughly dug in the fall, and the soil is mixed with compost and fertilizer.
For autumn work, the site is prepared in the spring or summer. Holes for planting seedlings are dug 2-3 weeks beforehand. The holes should be at least 60 cm deep and 70 to 90 cm wide. Small stones or crushed stone are placed in the holes, and the soil is mixed with organic and nitrogen fertilizers.
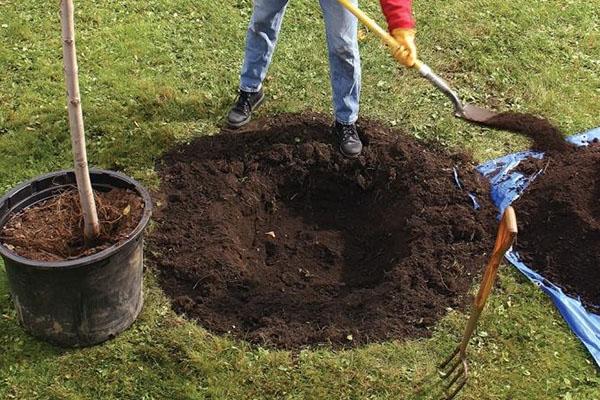

Technology of planting seedlings
To avoid making a mistake when choosing seedlings, it's best to purchase them from reputable garden centers and nurseries. The seedlings are carefully inspected for damage, diseases, and pests. The plants' rhizomes should be well-developed and moist, free of damage, lumps, and growths.
- Before planting in open ground, plants are immersed in settled, warm water for 3-4 hours, and then treated with a solution of manganese or special antibacterial preparations.
- Prepared fertile soil is poured into the bottom of the hole, a small depression is made and a support is placed to support the plant.
- The seedling is placed in the hole, its roots are carefully spread out, and covered with soil. There should be no space between the roots and the soil.
- The soil around the tree is carefully compacted and watered.
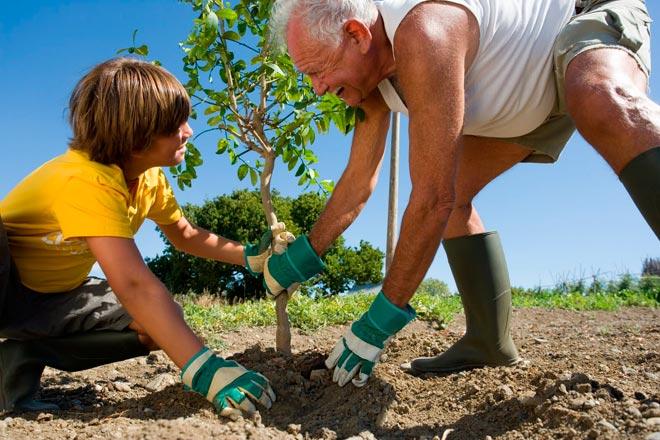 Important! The point where the seedling's trunk meets the rhizome is called the root collar. When planting, the root collar remains 5-7 cm above the soil level.
Important! The point where the seedling's trunk meets the rhizome is called the root collar. When planting, the root collar remains 5-7 cm above the soil level.
Fertilizer and watering
Trees are watered 4-5 times throughout the season. The first watering occurs immediately after planting the seedlings in open ground. The next watering occurs 7-10 days later. Subsequently, apple trees are watered thoroughly once a month. During droughts and extreme heat, irrigation is carried out more frequently.
Fruit crops are fed with organic, mineral and nitrogen fertilizers.
Organic fertilizer is applied once per season. During the growing and development period, trees require nitrogen supplements. Before winter dormancy, phosphorus-based fertilizers are added to the soil.
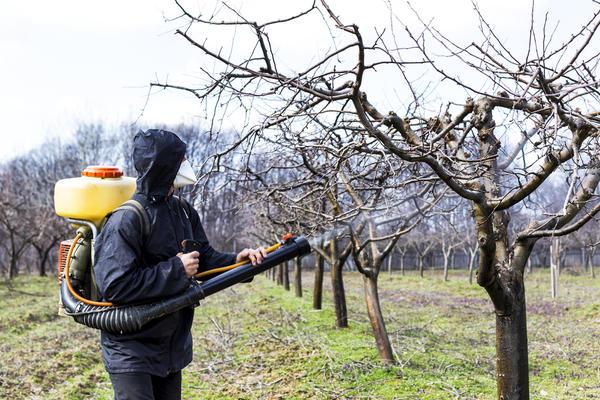
Preventive treatment
To prevent pests and diseases, fruit trees are sprayed prophylactically every spring and fall. In spring, treatments are carried out before flowering and fruit set. If repeat treatments are necessary, they are carried out after flowering. Fungicide-based products or solutions of soap and tobacco are used for this purpose.

Pruning and crown shaping
The first formative pruning is carried out immediately after planting the tree in open ground. Since the tree's crown is elongated, all branches are trimmed 5-7 cm below the main trunk. formative pruning of apple trees Macintosh is carried out as needed.
Sanitary pruning is carried out every spring and fall. Damaged, dried, broken, and frozen branches are removed from the trees.
Preparing the tree for winter
Before the winter holidays, the following activities are carried out:
- The tree trunk circle is carefully loosened, hilled and mulched with peat, sawdust or dry leaves.
- The tree trunk is treated with whitewash or lime.
- To prevent damage to the bark by rodents and small animals, the lower part of the trunk is wrapped in mesh or covered with a special material.
- In regions with snowy winters, a large snowdrift forms under the tree, which will protect the horses from freezing.
 Important! If the summer and fall were dry, water the apple trees generously before wintering.
Important! If the summer and fall were dry, water the apple trees generously before wintering.
How to propagate a tree
Apple trees of the McIntosh variety are propagated by cuttings, air layering, or by grafting cuttings onto a suitable rootstock.
- The easiest way to propagate apple trees is by cuttings. This involves pruning the tops of mature tree branches, planting them in pots until the first roots appear, and only then transplanting them into the open ground.
- To propagate by air layering, make a cut at the base of a strong, healthy branch in the spring. Next, fill the cut with peat and wrap it tightly in plastic. Until the first roots appear, moisten the peat as needed.
- Grafting cuttings is a complex and labor-intensive method of propagating apple trees, which only experienced gardeners can handle.
Related varieties
Numerous varieties of this fruit crop have been developed from the Mackintosh apple variety. Many hybrid varieties are frost-resistant, making them suitable for cultivation even in northern climates.
Daughter Mackintosh
The Mackintosh apple tree, a variant of the "Daughter" variety, was bred by Russian breeders for increased cold tolerance. This fruit tree is known for its abundant yields and long-lasting shelf life. It begins bearing fruit five years after planting. The tree produces green fruits with a bright red blush.
Black
The Black variety is another frost- and drought-resistant apple tree. The first harvest occurs four years after planting. The tree grows small, which is an advantage for small garden plots. The fruits are medium-sized, yellow-green, with juicy, sweet flesh and a slight hint of tartness.
Cortland
One of the oldest varieties of the Mackintosh variety, Cortland apple trees were introduced to Europe at the beginning of the last century and are still actively grown by gardeners and farmers. The only drawback of this fruit tree is its poor resistance to scab.
American Macintosh
The American McIntosh variety is a small apple tree with bright red, juicy, and sweet fruits. This fruit, a storehouse of vitamins and nutrients, is used for baby food and dietary nutrition.











