- Selection and cultivation area of the Spartak apple tree
- Methods of growing fruit crops
- On a dwarf rootstock
- Columnar
- Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- Characteristics and description
- Size and annual growth
- Crown and branches
- Foliage and buds
- Fruiting of the tree
- Flowering and pollinators
- Ripening time and yield per tree
- Harvesting and storage
- Tasting evaluation of the fruit and the scope of application of apples
- Transportability
- How does an apple tree tolerate low temperatures and drought?
- Susceptibility to diseases and pests
- Landing specifics
- Required soil composition
- Selecting and preparing a landing site
- Dimensions and depth of the planting hole
- Timing and step-by-step algorithm for planting a seedling
- Further care
- Watering mode
- We apply fertilizers
- We trim and shape the crown
- Loosening and mulching the tree trunk circle
- Prevention and protection of wood
- Covering for the winter
- Methods of reproduction
- Gardeners' reviews of the Spartak variety
The apple tree is one of the most common fruit trees grown in orchards across the globe. Its adaptability to any climate and the unique qualities of its fruit have earned it a place among gardeners. Breeders have developed a wide variety of cultivars with distinct technical characteristics and flavors. The Spartak apple tree ranks high among this diversity and is popular among experienced gardeners.
Selection and cultivation area of the Spartak apple tree
The Spartak apple tree is based on the Sharopai variety. Breeding efforts to develop the variety were conducted at the Kuibyshev Experimental Station and were successful in 1945. In 1959, the variety was included in the Register of Breeding Achievements. Its creator was S. P. Kedrin.
Methods of growing fruit crops
To increase frost resistance, it is recommended to grow the Spartak variety on a winter-hardy dwarf or columnar rootstock.
On a dwarf rootstock
An apple tree on a dwarf rootstock grows no more than three meters in height. Its small size makes caring for the tree and harvesting easy. This method is suitable for growing in areas with low groundwater levels.
Dwarf apple trees are the result of grafting clonal scions of a certain variety onto dwarf rootstocks.
Columnar
Columnar apple trees are small trees up to 2.5 meters tall and no more than 0.5 meters wide. They lack the traditional long lateral branches. These medium-sized columnar apple trees are the result of grafting common varieties onto superdwarf rootstocks.

Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The main advantages of the Spartak apple tree are:
- early maturity;
- high level of fruiting;
- stability of crop size;
- the taste of apples.
The main disadvantage is weak immunity to diseases such as scab.
Characteristics and description
The Spartak apple tree adapts well to any climate and growing conditions. It is hardy and undemanding in terms of light and moisture.
Size and annual growth
Spartak is a medium-sized tree. At maturity, it doesn't exceed six meters in height. This size makes pruning and harvesting easy.
Crown and branches
This variety has a pyramidal crown. It is very dense and requires pruning. The skeletal branches are positioned at an acute angle, so they often break during squalls and heavy snowfalls.

Foliage and buds
The leaves are oblong, wavy at the edges, and have a strongly elongated, often curled tip. The leaf margins are doubly serrated. The underside is covered with light pubescence.
The variety is characterized by increased excitability of the buds, which affects the high level of fruiting.
Fruiting of the tree
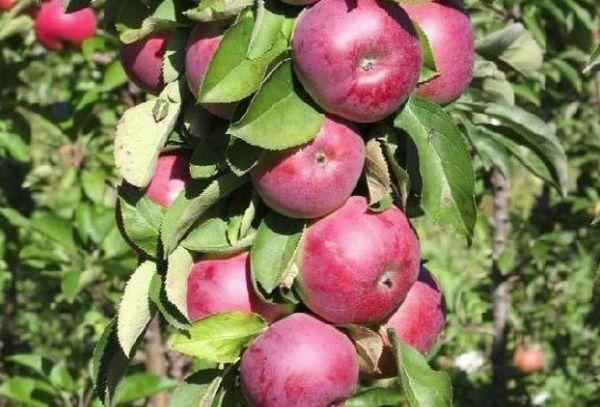
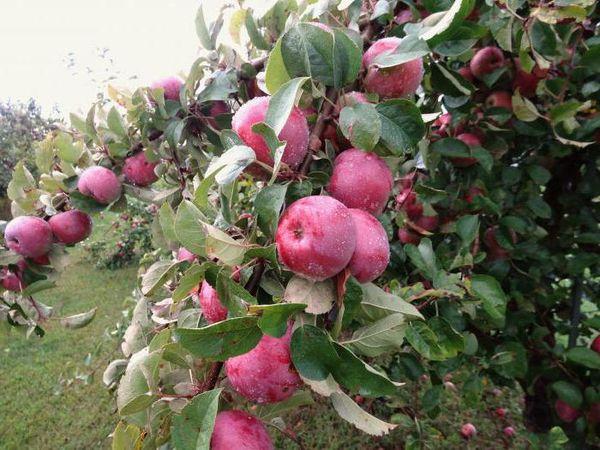
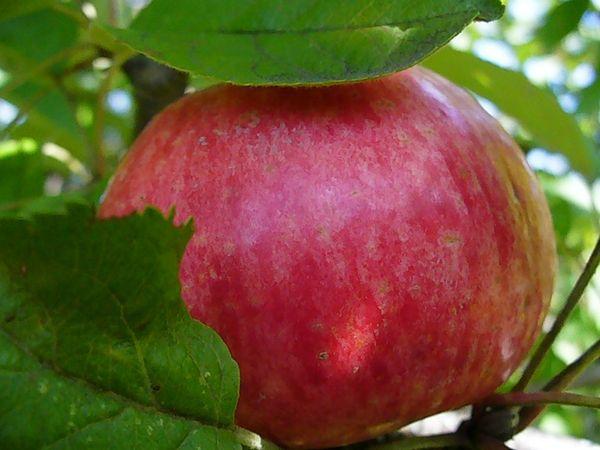
The Spartak variety bears fruit evenly and annually, producing delicious yellow-green apples with a bright, washed-out blush. Due to their small size, the light spots under the skin are virtually invisible. The apples are round-conical in shape. The flesh is white and firm. The apples' acidity is barely noticeable.
The average apple weight is 130 grams. The maximum recorded weight is 300 grams. Young trees produce large apples. Fruiting is uneven in some years. To increase yield, the tree requires periodic pruning.
Flowering and pollinators
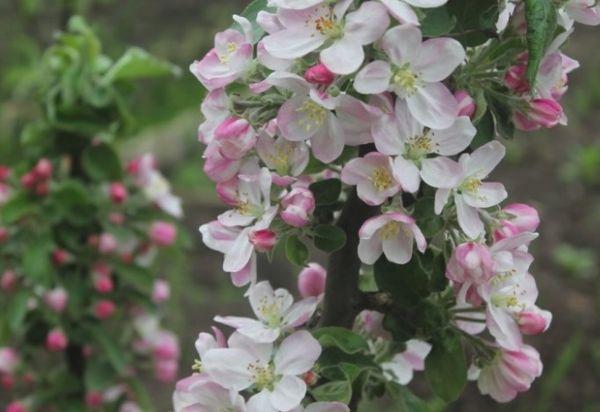
This fruit crop is self-pollinating, but cross-pollination increases yield. Suitable varieties for cross-pollination include Calville Snow, Umanskoye, and Idared.
Flowering times depend on the local climate. Flowers open at a rapid pace and bloom profusely.

Ripening time and yield per tree
The first apples are ready for consumption as early as early September, with the remainder ripening within three weeks. The bulk of the harvest is collected in mid-September. The Spartak variety is highly productive. A single mature tree can yield up to 100 kg of apples.
Harvesting and storage
Ripening and harvesting occur unevenly. Apples are determined to be ripe by a uniform red coloration of their skin.
When stored at 0°C in a dry place, sorted apples will keep well for up to five months. However, after just two months, their flavor begins to change.
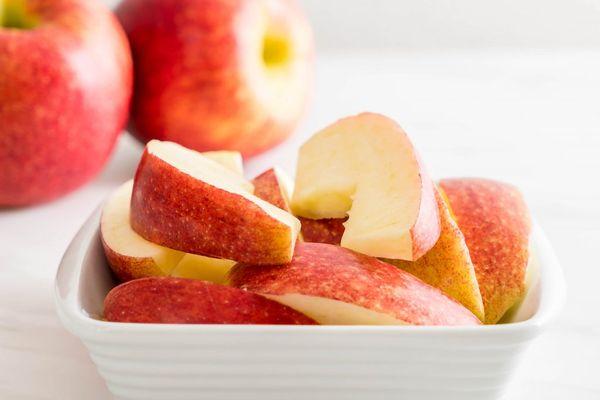
Tasting evaluation of the fruit and the scope of application of apples
This apple tree is worthy of gardeners' attention—it received a tasting score of 4.5 out of a possible five. Spartak apples have a wide range of uses. They are delicious fresh, suitable for canning, and for making various beverages.

Transportability
Apples tolerate transportation well and are stored for a long time.
How does an apple tree tolerate low temperatures and drought?
Thanks to its drought and frost resistance, this variety can be grown equally effectively in any region. It tolerates temperatures down to -25°C. In regions with cooler temperatures, it requires reliable winter protection.
The Spartak apple tree tolerates drought well and can go for long periods without watering.
Susceptibility to diseases and pests
In unfavorable years with prolonged rainfall, the Spartak variety can be susceptible to scab. It is very rarely affected by cytosporosis and fruit rot.
Landing specifics
Spartak has a wide crown, so it is planted no closer than five meters from other trees.
Required soil composition
Apple trees require porous soil with a pH of 5 to 7.5. Soils with different pH levels can be adjusted to the required parameters. Black soil, sandy loam, and loamy soils are ideal.
 When planting, add peat, compost, humus, sand, and mineral fertilizers to the excavated soil. The proportions depend on the soil characteristics.
When planting, add peat, compost, humus, sand, and mineral fertilizers to the excavated soil. The proportions depend on the soil characteristics.
Selecting and preparing a landing site
The location of an apple tree is crucial. Avoid planting a young apple tree in the same place as an older one. The accumulated glycoside in the soil negatively impacts the seedling's growth. Apple trees thrive if plum or cherry trees were previously grown in the same location.
To plant a young seedling, the site must be carefully prepared. Clear it of old grass and debris. Dig a hole for planting well in advance. It's best to prepare the hole six months before planting.
Dimensions and depth of the planting hole
An apple tree will require a large planting hole. It should be 1.5 meters deep and two meters in diameter.
Timing and step-by-step algorithm for planting a seedling
Planting timing depends on local conditions. In regions with early frosts and autumn snow cover, early spring is preferable. In areas with a mild climate and a long autumn, planting timing is a matter of personal preference.
Landing is performed in the following sequence:
- the dug hole is filled with fertile soil;
- a small mound is formed on it, the dimensions of which correspond to the root system of the seedling;
- the roots of the seedling are spread evenly over the mound and covered with soil, compacting it;
- The hole is thoroughly watered with water with the addition of a rooting agent.
The seedling is tied to a peg driven deep into the ground.

Further care
The Spartak variety is low-maintenance. Periodic fertilization, timely pruning, and preventative treatments are often sufficient to grow a healthy tree and produce fruit.
Watering mode
Apple trees are watered as the soil dries out. The watering schedule and amount depend on the local conditions.
We apply fertilizers
To maintain high fruit production and grow a healthy tree, it is fertilized periodically. Nitrogen fertilizers are used in the spring, and mineral fertilizers in the fall.
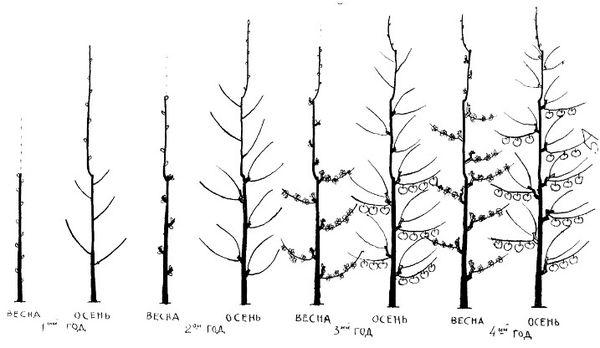
We trim and shape the crown
When growing the Spartak apple tree, crown formation is of paramount importance. In the first year, four skeletal branches are left and shortened to three buds. All remaining branches are pruned. In subsequent years, all weak, crooked, and crowding branches are removed.
Loosening and mulching the tree trunk circle
After heavy watering or heavy rain, the soil needs to be loosened. To avoid periodic loosening, gardeners mulch the soil with sawdust, straw, or dry leaves.
Prevention and protection of wood
To prevent fungal diseases, treat the tree with a copper sulfate solution in early spring and fall. Insect control is achieved with a urea solution or C30.
To protect against insect invasion during fruiting, gardeners use folk remedies.
Covering for the winter
To prevent apple trees from freezing in winter, they are insulated with covering materials. The area around the tree trunk is mulched with a thick layer of humus or straw. Covering is especially important in regions with prolonged frosts below -20°C.

Methods of reproduction
The following methods are used for reproduction:
- cuttings;
- layering;
- vaccination.
For the development of new varieties in nurseries apple trees are grown from seeds.
Gardeners' reviews of the Spartak variety
According to user reviews, the Spartak apple tree is easy to care for. It requires protection from pests and scab. Pests are most common in regions with mild climates.
Thanks to its flavor, aroma, and juiciness, the Spartak apple tree has become a popular choice for garden plots across Russia. It is tolerant of weather conditions and requires little care.











