- Description and Features
- Vine
- Inflorescences
- Berries
- Taste
- Growing region
- History of selection
- Main characteristics
- Drought resistance
- Frost resistance
- Applications of berries
- Resistance to diseases and pests
- Varieties
- Black
- Pink
- White
- Nutmeg
- Pros and cons of the variety
- How to plant correctly
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Choosing a location
- Soil requirements
- Site preparation
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering mode
- Top dressing
- Protection from rodents
- Preparing for winter
- How to protect crops from birds
- Mulching
- Trimming
- Preventive spraying
- Weeding and loosening
- Methods of reproduction
- Diseases and pests
- Harvesting and storage
- Application in winemaking
- Tips from experienced gardeners
Sauvignon grapes are among the most popular in the world. They are grown practically worldwide. Currently, efforts are underway to introduce them to Russia. The berries have a tart and distinctive flavor, but they are used in winemaking to create beverages. Sauvignon is the second most popular wine grape variety.
Description and Features
The variety description includes the vine, flowers, berries, flavor, and growing region. You can grow this grape in your own garden. However, optimal conditions are required. Sauvignon Sauvignon is a wine grape.
Vine
Grape bushes form vines. This is a characteristic of this crop's growth. These vines consist of long branches that are attached to a trellis. From these branches, foliage extends and bunches of grapes hang down.
At the beginning of the growing season, grape vines have a reddish-green hue. Later, they turn green and then become covered with bark. Woody vines bear fruit for several years in a row. The foliage is green, with large blades dissected into 3-5 parts.
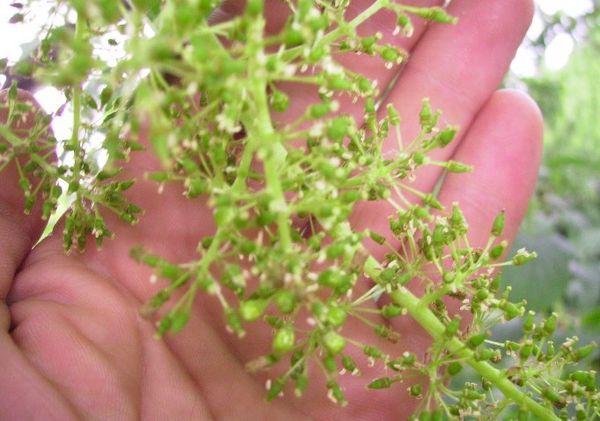
Inflorescences
The inflorescences are densely clustered. The flowers are white, with pointed petals. After flowering, berries form. Fruit forms in almost every flower's place. Flowering is long, and the variety is considered a mid-season grape. Harvesting begins in September or October.

Berries
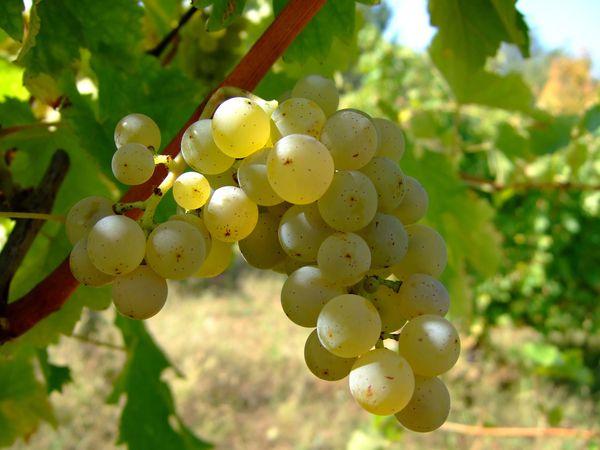
The fruits are collected in cylindrical or conical clusters weighing up to 150 g. Each berry weighs 3 g and is tightly packed together. The grapes are light yellow or green in color. The shape of the grapes is elongated and oval. The grapes do not fall off, and ripening takes about 1.5 months.
Taste
Sauvignon is one of the most popular varieties. Its flavor is excellent. The grapes contain a fair amount of sugar and vitamin C. The berries have a pleasant sweet taste.
Growing region
After its development, the grape variety was distributed worldwide. However, not all countries offer optimal growing conditions due to varying climates. It is most widely grown in:
- Bulgaria;
- Montenegro;
- USA;
- Africa;
- France;
- Italy;
- SOUTH AFRICA.
Important! Recently, attempts have been made to grow Sauvignon in Russia.

History of selection
The Sauvignon grape was developed in France. It is currently the second most popular grape in the world after Chardonnay. The variety was created through natural crossing of Tramner and Chenin Blanc grapes. The entire process took place in the Loire Valley. In the mid-19th century, Sauvignon spread throughout almost the entire world in a relatively short period of time.
Main characteristics
To start growing grapes on your own plot, you need to thoroughly study their characteristics. Different regions require specific adaptations to their environment.
Drought resistance
The grapevine's heat tolerance is average. It prefers a moderately warm climate. Its roots are not well developed enough to draw water from the soil. If planted in the south, Sauvignon vinifera will require regular and supplemental watering.
Frost resistance
The plant can survive temperatures down to -25°C. The root system is mulched for the winter, and the vines and shoots are covered with breathable insulating materials. Otherwise, the bush will freeze and will have to be replanted. In the worst case, the vine's roots will die, and the plants will need to be replanted.

Applications of berries
Sauvignon grapes are processed into wine, grape juice, and other juice-containing products. This variety is a commercial grape. After harvest, the berries are not stored but sent directly for processing.
Some varieties of elite wines are made from this grape:
- Chateau Los Boldos;
- Sotters;
- Madfish;
- Late Harvest.
The wine typically contains 13% alcohol by volume or more. It has a light gooseberry aroma and a tart flavor. The resulting wines include dry, semi-dry, semi-sweet, and sweet varieties.
Sauvignon doesn't keep fresh for long, even in bunches. When growing it in your own garden, you need to plan for its prompt processing.
Resistance to diseases and pests
The vineyard has strong immunity to virtually all diseases common to this crop. Its only enemy is gray mold. Leaf rollers are also occasionally found. With preventative measures, Sauvignon is disease-free.
Varieties
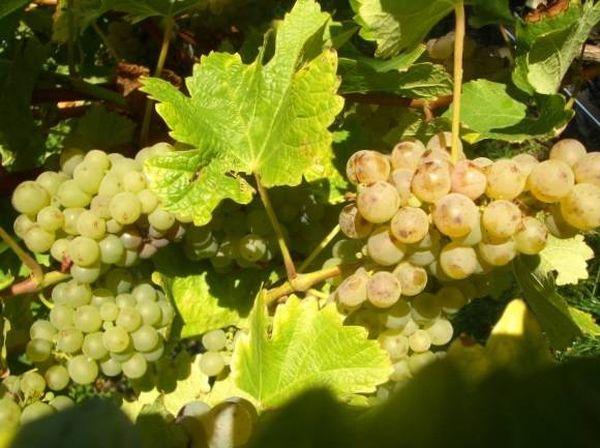
Sauvignon has its own grape varieties. It comes in black, pink, white, and Muscat varieties.

Black
This mid-season variety produces large bunches of grapes, up to 400 grams each. The berries are small and slightly elongated. The bush is medium-sized and thrives in the south, yielding up to 60-70 liters of berries per plant. The fruit is dark purple, almost black. It is used to make red wines.
Pink
Sauvignon Gris produces pink-hued berries. Ripening time is mid-season, with harvesting occurring in late September or early October. The vine is medium-sized and grows well on a trellis. This grape is used to produce rosé wines, which have a light pink hue.
White
The fruit ripens in mid-autumn. Suitable for growing in southern regions, it produces small clusters weighing up to 180 g, cylindrical or conical in shape. It is moderately resistant to frost and drought. It has a strong immune system and rarely gets sick.

Nutmeg
A special hybrid variety. Its berries have a light pink blush. The bush smells of Muscat. It ripens mid-season, producing small berries, up to 3 grams each. They are gathered in dense clusters weighing 200 grams. The grapes are used to make Muscat wines.
The majority of wines are made from white and black grapes.
Pros and cons of the variety
Each grape variety has its own advantages and disadvantages. It's recommended to research these before planting in your garden. The positive aspects include:
- easy care;
- high yield;
- disease resistance;
- adaptability to new conditions;
- average shedding;
- special taste.
Gardeners note the following disadvantages:
- bright, tart taste;
- tendency to pea;
- tendency to shedding;
- short-term storage.
How to plant correctly
Proper vine planting is the key to a good harvest and a healthy vineyard. To ensure proper planting, it's recommended to research the selection of seedlings, planting location, and planting techniques.
Recommendations for choosing deadlines
Fall or spring are ideal times for planting grapes. Early spring planting is successful, and the vines have time to root well before winter. However, this doesn't guarantee winter survival. Young seedlings will have a hard time surviving frost.
Therefore, it is recommended to plant in the fall, preferably mid-October. By this time, the bush will have sufficiently established roots and adapted to winter frosts.
Choosing a location
The best location for a vineyard is a south-facing site with consistent sunlight. Choose an elevated site to protect the roots from flooding during rainfall.
Soil requirements
Loamy or sandy loam soil is preferred. If it has a sandy or clayey texture, add sand to create a raised bed. Drainage is placed at the bottom of the planting hole to ensure additional drainage.
Site preparation
The planting site can be prepared in advance. To do this, dig it up, remove weed roots and stones, and mix it with sand if necessary. Adjust the soil pH. Grapes require a neutral or slightly acidic pH. They are unlikely to bear fruit normally in other conditions.

How to select and prepare planting material
When purchasing grape seedlings, it's best to purchase them from reputable specialist stores and nurseries. Pay attention to the condition of the:
- root system;
- foliage;
- shoots and vines;
- scion sites.
All areas of the seedling should be moist, free of spots, cracks, chips, cuts, or scratches. The roots and leaves should be healthy, free of plaque and other suspicious signs.
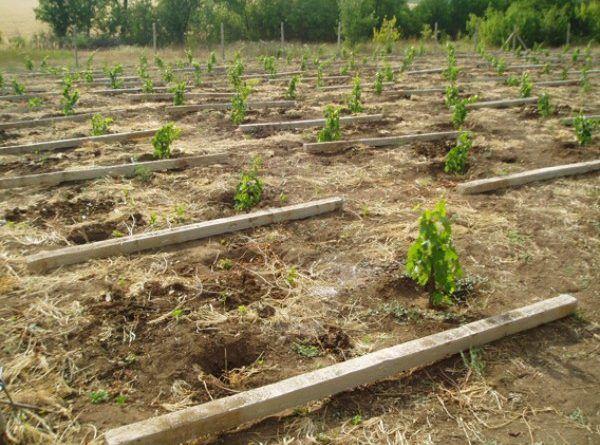
Planting diagram
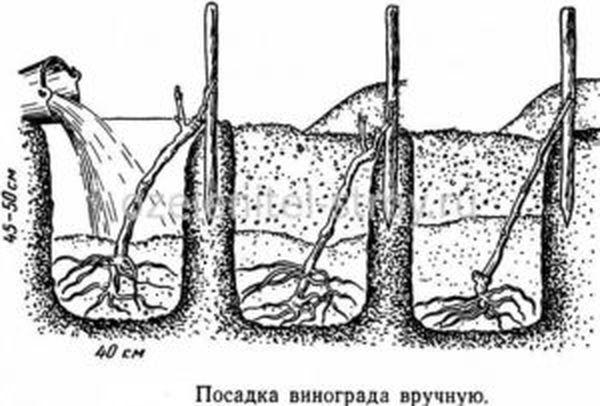
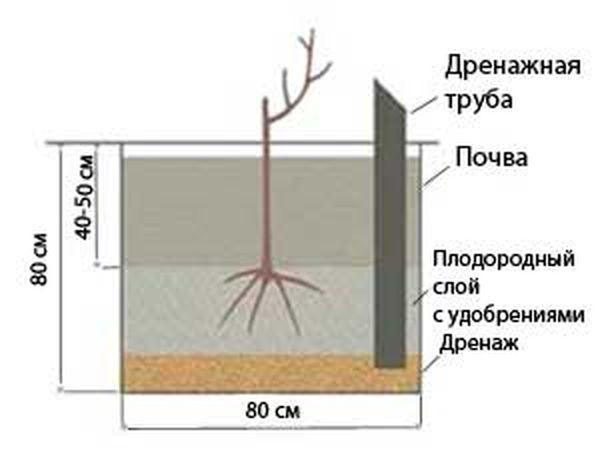
Plant the seedlings 1.5 meters apart, as the plant will eventually grow in different directions. This will help prevent the vines from becoming tangled. Planting follows a specific pattern:
- Dig a hole 70 cm deep and 50 cm in diameter.
- Place 40 cm of peat on the bottom to create drainage.
- They place a seedling in it.
- Sprinkle with soil and compact.
- Then add 300 g of potassium fertilizers and superphosphate.
- Cover with soil and compact.
- Pegs are driven in along both edges of the planting and the plant is tied.
- They water the bush.
- Mulch using sawdust, straw, cut grass, and moss.
Important! It is recommended to install it in advance. trellises on a vineyard plotto avoid damaging the bush during transplantation and installation of the structure.
Care instructions
Sauvignon grapes, like other crops, produce high yields when properly cared for. This includes proper watering, fertilizing, protection from rodents and birds, pruning, weeding, loosening, and spraying.
Watering mode
The plant doesn't like frequent watering. This procedure is performed three times per season:
- immediately after removing the winter cover;
- during flowering;
- during the fruiting period.
In between, repeat watering only during prolonged droughts and when the soil at the roots becomes dry. Overwatering increases the risk of gray mold developing.
Top dressing
If fertilizer was added to the soil at planting, there's no need to repeat the application for the next 3-4 years. Organic or mineral fertilizers are then added. Suitable organic fertilizers include:
- wood ash;
- compost;
- manure;
- humus.

Of the minerals, grapes respond well to:
- ammonium nitrate;
- urea;
- potassium compounds;
- superphosphate.
Excess fertilizer leads to the death of the plant; do not increase the dosage.
Protection from rodents
To protect against small rodents, special poisons are used. According to the instructions, they are placed on the soil under the bush. They repel the pests and, if they approach, kill them.
Preparing for winter
Preparing a vineyard for winter involves several stages:
- root mulching;
- protecting vines from frost using spunbond or agrofibre;
- pre-winter watering;
- application of fertilizer.

How to protect crops from birds
Birds often enjoy feasting on the grape harvest. To protect against their attacks, each bunch is covered with a special net. This net allows air and light to pass through without impeding the ripening of the berries.
Mulching
Mulch helps retain moisture and nutrients near grape roots, while also protecting them during winter. A variety of materials are used for this purpose:
- straw;
- peat;
- chopped grass;
- moss;
- sawdust.
The selected composition is spread in an even layer around the trunk of the bush.
Trimming
Pruning grapes — is a mandatory procedure for maintaining high yields and the health of the crop. After planting, the bush is trained every spring for three years. In the fall, sanitary pruning is performed. Dry leaves, weather-damaged areas of the vine, and branches growing in the wrong direction are removed.
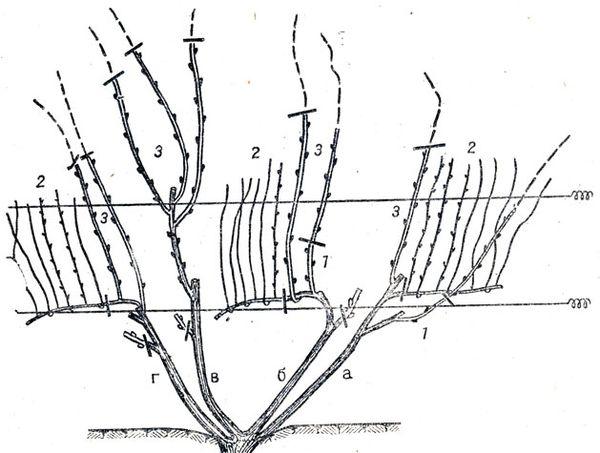
In summer, thinning pruning is done if necessary. The vine is inspected and excess shoots are cut off in dense areas.
Preventive spraying
To prevent grapes from becoming infected with fungi and leaf rollers, spray the plants with fungicides and insecticides in the spring, before the sap begins to flow. This will ensure a healthy harvest.
Weeding and loosening
Weeding and loosening the soil around the grape roots are essential. These manipulations help preserve the plant's required amount of nutrients. This is done as weeds emerge and a crust forms above the soil surface.
Methods of reproduction
Sauvignon can be propagated using vine sections, scions, or seeds. The simplest method is from seed. The seeds are dried and stratified. Then they are planted in the garden. Only the most viable ones will germinate.
Diseases and pests
Sauvignon grapes are almost never susceptible to disease. Gray mold is a common culprit. This fungus thrives in high humidity, causing a gray, fluffy coating to appear on the berries, vines, and leaves. This disease can be controlled with a fungicide.
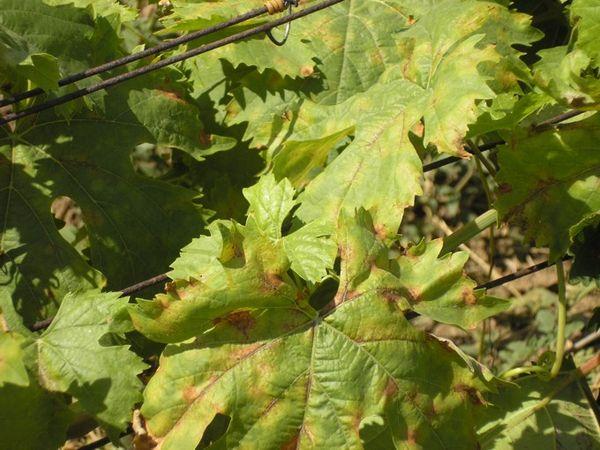

Leaf rollers are the main enemies of grapes. Their larvae are stored near the roots of the plant. After hatching, the beetles feed on the leaves and fruit. They can be controlled with insecticides and by destroying their nests.
Harvesting and storage
The grape harvest is from late September to mid-October. It cannot be stored for long, a maximum of seven days. Therefore, it is processed into juice and wine.
Application in winemaking
This grape variety is used to make a wide variety of wines. It is grown throughout the world. Due to its wide variety, it is used to make rosé, red, white, and Muscat wines. This wine has a shelf life of 1-3 years.
Tips from experienced gardeners
For beginning gardeners, you can listen to some useful tips:
- You shouldn't overwater or overfeed the grape bush, it may die.
- Preventative treatments are best carried out annually, as the weather is always unpredictable.
- Sauvignon wine loses its flavour over the years, so it should be used within 3 years.
- It is worth considering that this grape variety does not store well, and its taste does not allow it to be consumed fresh.











