- History of selection
- Description and Features
- Characteristics of the variety
- Frost resistance
- Drought resistance
- Productivity and fruiting
- Applications of berries
- Disease resistance
- Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- How to plant correctly
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Site selection and preparation
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Age
- Root system
- Length
- Vine
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering mode
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Protection from birds and insects
- Preparing for winter
- Preventive spraying
- Mulching
- Garter
- Methods of reproduction
- Burying the shoots
- With cuttings
- Grafting
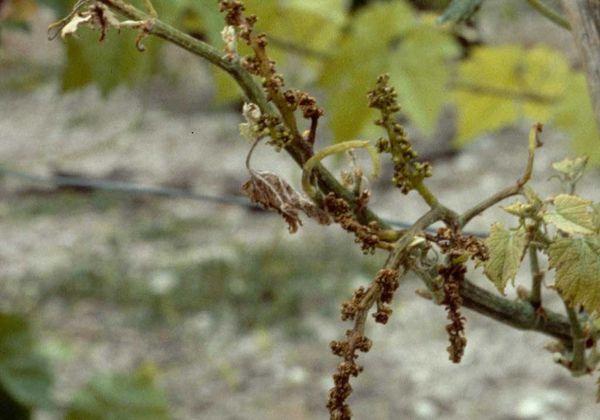
- Diseases and pests
- Anthracnose
- Bacterial cancer
- Escoriosis
- Grape mite
- Scale insect
- Withered sleeves
- Harvesting and storage
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
The Nadezhda Azos grape variety remains one of the most popular among gardeners. Its pleasant flavor and low maintenance requirements have earned it a place among the leading grape varieties for many years. The berries retain their flavor and appearance in any climate and weather. This variety is easy to care for, making it a popular choice among novice gardeners.
History of selection
The Nadezhda Azos grape variety was developed in the 1970s. The place where it was developed, giving it its name, is the Anapa Zonal Station of Horticulture and Viticulture (now known by a different name). The variety was developed by Nadezhda Nikitichna Apalkova.
Scientists have crossed two known species grapes - Cardinal and MoldovaThe result was a variety that inherited the best qualities of its parents. From the Cardinal, it inherited excellent flavor and relatively early ripening. From the Moldovan, the new variety inherited high yield, good pest and disease resistance, and abundant fruiting.
Due to numerous trials and then the perestroika period, the new grape variety remained unregistered for a long time. It was only in 1998 that it was added to the State Register, but its cultivation was restricted to the North Caucasus region.
The variety subsequently spread to other regions and grows well everywhere, including the Moscow region and even Belarus. It presents little challenge to gardeners and requires cover only in the most adverse weather conditions.

Description and Features
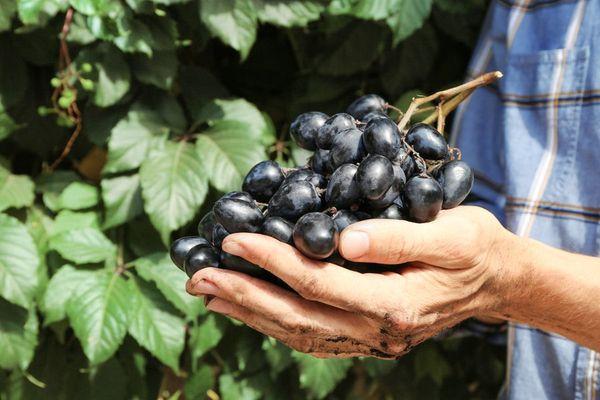
The Nadezhda Azos grape vines are known for their vigorous and strong growth, so they require pruning and shaping. The leaves are large and densely pubescent. They are dark green and have three to five lobes.
The conical bunches of this variety are characterized by a loose structure and thick stems. The weight of a single bunch ranges from 500 to 900 g. Cases have been recorded where the bunches have weighed up to 2 kg or more. The older the vine, the larger the bunches it produces.
The grapes are oval, dark blue, and slightly elongated. The skin is medium-thick but edible, covered with a velvety bloom. The fruits of this variety are considered large, reaching 25-28 mm in diameter and 8-9 g in weight.
The Nadezhda Azos variety has a pleasant flavor, dominated by sugar, but also with a hint of tartness. Tasters give it an 8.2 out of 10 for flavor. The berries are fleshy, with medium-sized seeds. They are very beneficial for health: they reduce the risk of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, prevent cancer, and strengthen the body's immune system. Unripe berries have a tart taste.

Characteristics of the variety
The Nadezhda Azos grape variety is a variety specifically bred for Russian gardeners. It possesses a number of characteristics that allow it to be grown in regions with a wide range of weather conditions.
Frost resistance
One of the variety's key qualities is its frost resistance. The grapes can withstand temperatures as low as -24 degrees Celsius.
At lower temperatures, the vine must be covered with non-woven material.
Drought resistance
Another advantage of Nadezhda Azos grapes is their resistance to prolonged drought. They produce a harvest without requiring excessive watering, even in soils dominated by clay and sand.
Productivity and fruiting
The variety's high yield (up to 90% of shoots) makes it popular with farmers and gardeners. One hectare yields from 150 centners to several tons of grapes, depending on the growing region. In gardens, up to 30 kg of berries can be harvested from a single bush. Not only the main shoots but also the side shoots bear fruit.
Applications of berries
The Nadezhda grape is not intended for winemaking. It is a table variety.
These tasty and healthy berries are recommended to be consumed fresh and unprocessed, or to be used to make various preserves: jam, marshmallows, compotes, and juice.

Disease resistance
This variety is popular because it is resistant to most fungal diseases. It has moderate resistance to some diseases, such as gray mold.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The main advantages of the variety are considered to be its properties:
- excellent taste and appearance;
- mid-early, and in warm regions early ripening;
- stable fruiting;
- good immunity to diseases;
- bisexual flowers and no need for pollination;
- good keeping quality and transportability.
The following characteristics are considered to be the weak points of grapes:
- in cloudy weather, pollination of flowers is weak;
- during heavy precipitation the skin of the berries cracks;
- the bushes are overloaded with bunches and are prone to pea-shaped flowers;
- cuttings do not root well.
How to plant correctly
Nadezhda Azos is an easy-to-grow plant. It doesn't require much care and requires minimal maintenance. However, beginners should consider a few planting and growing nuances to ensure a consistent harvest.

Recommendations for choosing deadlines
Planting on time is very important for this variety due to poor rooting of cuttings.
In any region, Nadezhda Azos grapes are planted in the spring: in the south – at the beginning of May, in cold regions – after the middle of the month.
Conditions for successful planting: warm air (not below 15 degrees), soil warmed up to 10 degrees and water for irrigation.
Site selection and preparation
For successful planting and rooting of cuttings, it's important to select a site and prepare it properly. The location should be sunny, open to the south, and sheltered to the north. Grapes require light for rapid growth. You can plant grapes near the walls of houses and other buildings facing south. These buildings will release the heat they've collected during the day to the plants at night.
It is better to protect the bushes from the north wind behind a fence or buildings.
It's important to consider the soil composition of the site. Grapevines should not be planted in marshy or saline areas or where rocky outcrops are close to the surface (less than a meter).

The vine feels good on sandstone and loam soils, and grows well on black soil.
It is not recommended to plant bushes next to other grape varieties, as cross-pollination can affect the characteristics of the hybrid.
To prepare the site, the following steps must be taken:
- Clear the area of bushes and stones.
- Loosen the soil to a depth of 70-100 cm.
- If the soil is loose enough, the cuttings are planted in holes.
- If the soil is heavy, it is improved with humus, manure, crushed stone, and sand.
How to select and prepare planting material
Selecting seedlings for planting is no less important when growing grapevines. Experienced gardeners use specific criteria to separate good, healthy seedlings from poor ones.
Age
The best age for bushes is between 1 and 2 years. They are considered the most resilient. The younger the plant, the easier it will be to plant and adapt.
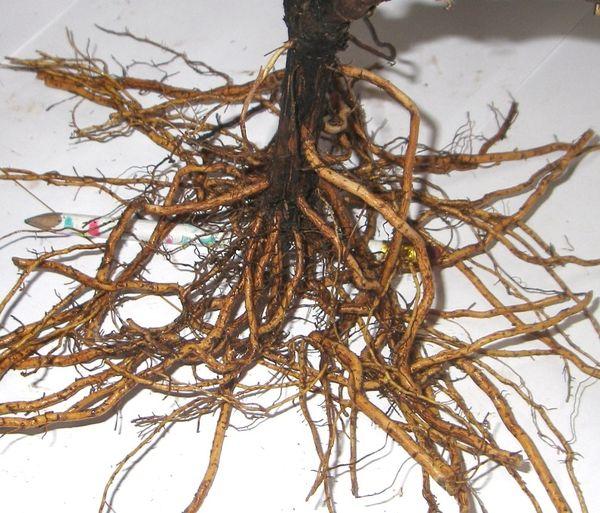
Root system
Healthy, strong seedlings should have 3-4 root shoots. The thicker and more flexible these shoots are, the more likely they are to survive.

Length
The most optimal length for grape seedlings is from 30 to 40 cm.
Vine
The appearance of the grapevine is also considered when planting. A healthy sapling has a perfectly straight trunk and undamaged bark. It may have one or two vines, but they shouldn't be too thin.
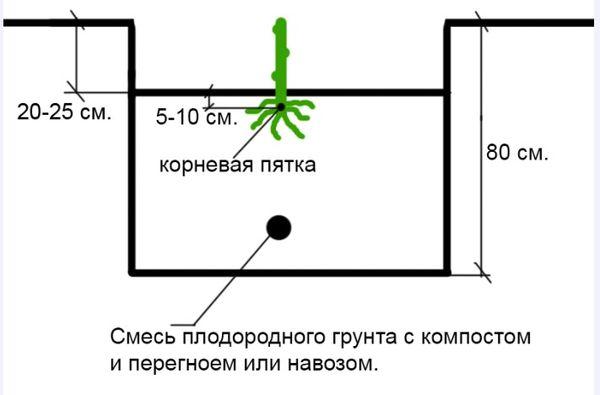
Planting diagram
Remove some soil from the hole prepared for planting. Place the plant in the center, spreading the roots so there are no air pockets underneath. Fill the hole with soil until the root collar (the point where the plant grows) is below ground level. Then compact the soil and water with two buckets of warm water.
A support is installed near the bushes. This will be used to support the young shoots. If the bush is growing next to a wall, it is planted at a slight angle, with the top facing the building.
Care instructions
The full development and timely fruiting of grapes depend on proper care. Caring for the Nadezhda Azos grape is easy; the key is to complete all the necessary steps at the right time.
Watering mode
The watering schedule for seedlings and mature plants differs. Young seedlings require regular watering to develop a strong root system. During the first month, they are watered weekly. From the second month until the end of summer, watering is reduced by half.
During the hot season, grapes are watered in the morning or evening.
Mature bushes don't require additional watering except during dry periods. They are watered after removing the plastic wrap, before and after flowering, and during berry formation. The first watering should be 200 liters, and subsequent waterings should be 20 liters per bush. If there was little rainfall in the fall, the plant will require an additional watering (200 liters) before winter.
Top dressing
When planting vines, all the necessary nutrients are added to the soil, so the plants don't need fertilizing for the next two years. Fertilizing is then carried out annually:
- Seven days before flowering, add a mixture of 10 liters of water and 2 kg of manure (or 50 g of bird droppings). If desired, you can fertilize with minerals: dissolve 65 g of nitrophoska and 5 g of boric acid in a bucket of water.
- Before fruit formation, plants are fed with the following mixture: ammonium nitrate (20 g) and potassium magnesium sulfate (10 g) are diluted in 10 liters of water. Repeat the feeding after a week.
- 10-14 days before harvesting, you can add a mixture to the soil, which is prepared as follows: add superphosphate (20 g) and potassium fertilizer (20 g) to 10 liters of water.
Trimming
Pruning grapes increases yield, improves fruit quality, and makes vine maintenance easier. This procedure is performed in the fall, a few weeks after leaf fall. At this time, sap flow stops, and the plant will not be harmed.
It is recommended to form 'Nadezhda Azos' into a single-arm cordon 1.2 m high. To prevent overcrowding, no more than 25 shoots are left on the bushes.
Protection from birds and insects
Birds and wasps can destroy half a grape harvest if left unchecked. To deter them, gardeners recommend placing rattles or scarecrows in their plots.

Mature brushes can be covered with fine mesh. Special traps are installed against wasps, and bioacoustic devices are deployed on large farms.
Preparing for winter
In regions where winter temperatures drop below -22°C (-72°F), the vines should be covered with plastic film. The film should be placed so that it doesn't touch the vines. Remove the film after all the snow has melted. In warmer climates, there's no need to cover the vines. Mulching the soil or insulating the roots is sufficient.
Preventive spraying
Despite its high resistance to many diseases, this variety requires preventative spraying. Treatment with anti-mite agents and fungicides is carried out before and after flowering.
The third stage of spraying is carried out during berry formation. It is recommended to spray from a distance of 30-40 cm.

Mulching
To keep the soil loose and prevent moisture evaporation, use mulch. Dry leaves, straw, or sawdust are suitable for this purpose.
Garter
Experienced gardeners recommend growing Nadezhda Azos using a single-plane trellis, as this is the most convenient and effective method of shoring up the plant. It's easy to install yourself. The wires on the trellis are tied so that the first row is 40 cm from the ground, with the remaining rows spaced every 45 cm.
Methods of reproduction
There are several methods for propagating grapes. Each gardener chooses the method that suits them best.
Burying the shoots
A healthy vine at ground level is pinned to the ground in the spring and covered with soil. By the end of the season, or the following spring, roots will appear at the pinned point, after which the vine can be cut from the mother plant and planted separately.
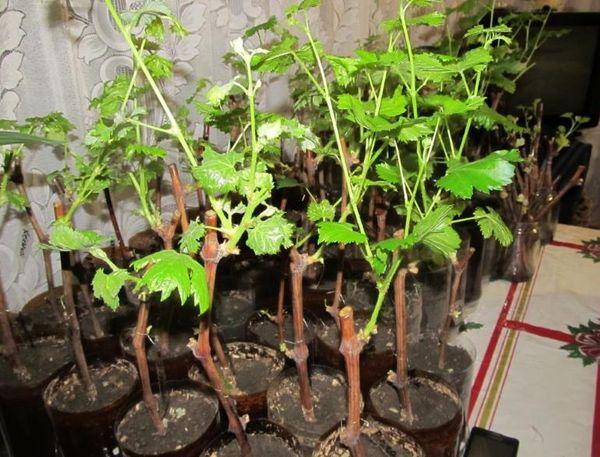
With cuttings
Most often, pre-prepared cuttings (saplings) are used for planting. There are several requirements for planting material. The cutting must have at least five buds, two of which are left above the soil surface when planting. The grapevine's root system must be developed, but without dry spots.

Grafting
Grafting grapes This is a rather complex process, so it's performed by experienced winegrowers. Typically, the variety is grafted onto a more robust rootstock to improve its winter hardiness.
Diseases and pests
The Nadezhda Azos variety is renowned for its resistance to fungal diseases. However, preventative measures won't hurt, and the first signs of infection require immediate action.
You can protect grapes from pests by taking preventative measures at the very beginning of the growing season.

Anthracnose
Red spots appear on grape leaves-brown spots that soon merge. They dry out. The disease affects all parts, and the flow of nutrients is disrupted. The inflorescences and berries die.
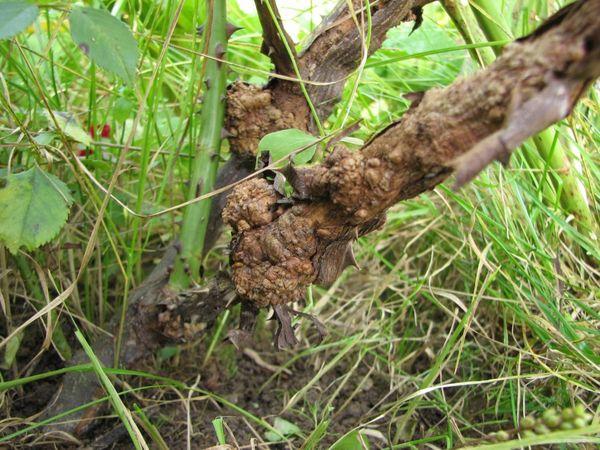
Bacterial cancer
White growths appear on the grapevine, which soon darken and harden. The bush stops growing and dies.

Escoriosis
A fungal disease that can destroy up to 50% of a vineyard.
Grape mite
Mites suck the juices from young grapevines, leaving punctures on the surface of the leaves. The leaves turn yellow and diseased. Infestation occurs when the vines freeze and experience high humidity.
Scale insect
Grapes are attacked by insects that feed on their sap. As a result, the plant develops poorly and is susceptible to infection.
Withered sleeves
Dead arm or spotted necrosis most often affects plants under cover, so the disease is difficult to detect in its early stages. The affected bush dies.

Harvesting and storage
Gardeners describe the Nadezhda Azos variety as a mid-early ripening grape. The berries ripen 120 or 130 days after bud swelling.
The vine buds and blooms noticeably later than other species, which is an advantage for growing in regions with variable weather conditions.
In the south, grapes ripen as early as mid-August, and in central Russia – at the end of September.
Grapes must be completely dry during harvest. If the bunches are cut too soon after rain, they will rot and spoil.
To cut the brushes, use sharp pruning shears.
This variety is known for its excellent berry preservation. They are placed in boxes on paper in a single layer, with the stems facing upward. This method allows the grapes to be preserved for up to two months, but they must be regularly checked for rot.
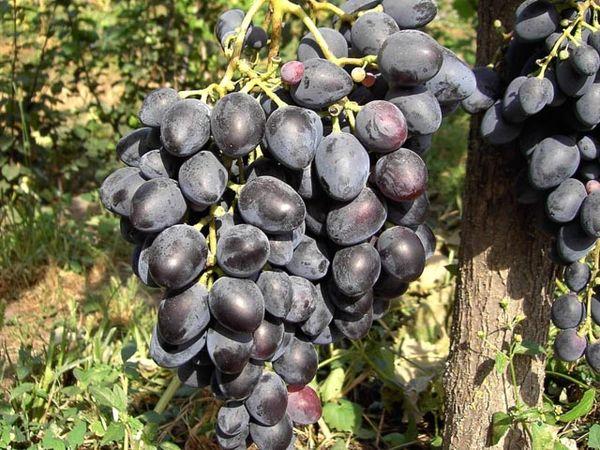

The best storage method is refrigeration, with temperatures down to -2°C and humidity up to 95%. The berries can be transported over long distances. These properties make this variety one of the most commercially viable.
Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
Experienced winegrowers know how to achieve consistent fruit production and improve the quality of this variety's berries. Here's what they recommend:
- The bushes need to be pruned promptly. Otherwise, the branches will become overloaded, and the bunches will not ripen fully. As a result, the gardener will end up with berries ranging from 5 to 10 mm in size.
- For better rooting of cuttings, it is recommended to soak them in water with added growth stimulator before planting.
- Nadezhda grows best with Moldova and Codryanka; other varieties are unsuitable. When planting different varieties next to each other, remember that vigorous varieties should not be placed near medium-sized ones. The former grow rapidly and deprive the latter of sunlight.
- Before wintering, grape vines are treated with copper sulfate and covered with manure.











